文档:https://github.com/typestack/class-transformer
class-transformer 是一个为 Typescript 设计的轻量级库,用于实现 JS 普通对象和类对象之间的转换。它基于装饰器模式,使得开发者能够定义如何将对象属性从一个形式映射到另一个形式,以及在转换过程中如何处理复杂的类型和嵌套的对象结构。有助于维护类型安全并提高开发效率。
举个 🌰:
假设我们定义了一个 User 类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| export class User {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
constructor(firstName: string, lastName: string) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
getName() {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
}
}
|
我们通过接口获取到一个 user 对象
1
2
3
4
| {
"firstName": "John",
"lastName": "Cage"
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
| fetch("user.json")
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((user: User) => {
console.log(user.getName());
});
|
注意:可以使用 User 定义类型获取到的 user 对象,且类型提示也可以使用;但是 user 只是普通对象,并不是 User 类的实例,所以不能使用 User 类中的方法
**解决方案**:
为了使用 User 类中的方法,我们可以自己这样处理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| fetch("user.json")
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((user: User) => {
const userInstance = new User(user.firstName, user.lastName);
console.log(userInstance.getName());
});
|
使用已有工具 class-transformer 进行处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import { plainToInstance } from "class-transformer";
fetch("user.json")
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((user: User) => {
const userInstance = plainToInstance(User, user);
console.log(userInstance.getName());
});
|
userInstance 打印结果:

3. 常用方法
3.1 plainToInstance(plainToClass)
将一个普通 js 对象转换为指定类的实例;第一个参数为要转换成的类定义;第二个参数是一个普通对象或者是对象数组;第三个参数为可选的转换选项
默认情况下,如果对象的属性和类的属性不匹配:
- 对象中有额外的属性(即类定义中没有的属性),转换的结果会包含这些属性
- 对象中缺少类定义中的属性,这些属性将被默认设置为 undefined
- 如果对象中属性和类定义的类型不匹配,会保留对象属性的值
3.2 instanceToPlain(classToPlain)
将一个类的实例转换为普通的 js 对象;第一个参数为类的实例;第二个参数为可选的转换选项
举例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import { instanceToPlain } from "class-transformer";
class User {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
constructor(firstName: string, lastName: string) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
getName() {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
}
}
const userInstance = new User("John", "Cage");
const userObj = instanceToPlain(userInstance);
console.log(userObj);
|
userObj 打印结果:只包含属性,不包含方法
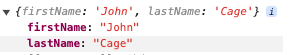
3.3 instanceToInstance(classToClass)
将一个类实例转换为一个新的类实例;第一个参数为类的实例;第二个参数为可选的转换选项
举例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import { instanceToInstance } from "class-transformer";
class User {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
constructor(firstName: string, lastName: string) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
getName() {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
}
}
const userInstance = new User("John", "Cage");
const userInstanceNew = instanceToInstance(userInstance);
console.log(userInstanceNew);
|
userInstanceNew 打印结果:拥有和 userInstance 相同的属性和方法(用于拷贝)
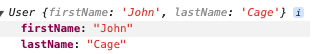
3.4 serialize
将类实例转换为 JSON 字符串;第一个参数为类的实例;第二个参数为可选的转换选项
即将废弃,不推荐使用,同 JSON.stringify
3.5 deserialize
将 JSON 字符串转换为类实例;第一个参数为要转换成的类定义;第二个参数为一个 JSON 字符串;第三个参数为可选的转换选项
即将废弃,不推荐使用,同 plainToInstance(cls, JSON.parse(jsonStr))
3.6 转换方法整理
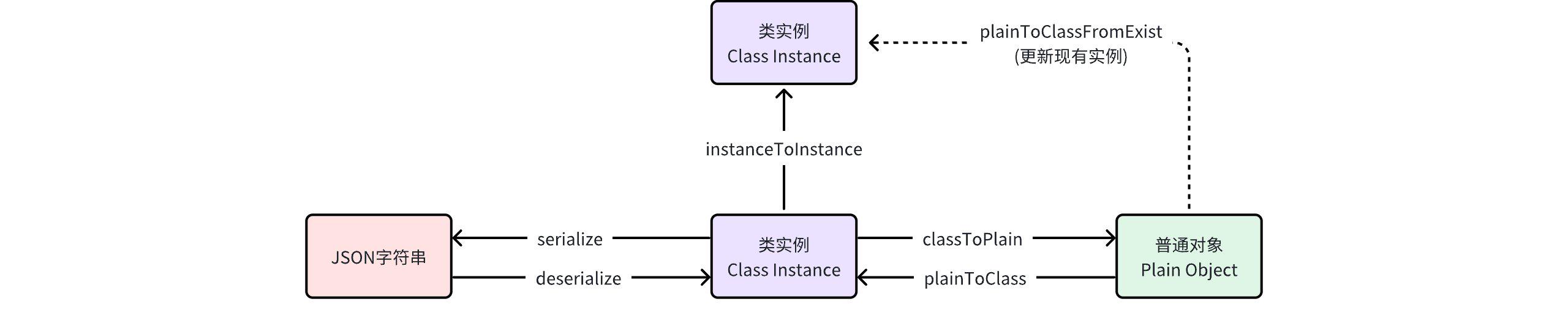
4. 装饰器及选项配置
- 装饰器:
- 用于自定义控制转换过程中的行为,比如哪些属性需要被包含、应该如何转换等等
- 选项配置:
- 转换方法的最后一个参数,允许你定制操作的具体行为。通常与装饰器配合使用
4.1 @Expose()
控制类的属性是否应该被包含在转换过程中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import { Expose, plainToInstance } from "class-transformer";
class User {
id: number;
@Expose()
firstName: string;
@Expose({ groups: ["admin"] })
lastName: string;
constructor(id: number, firstName: string, lastName: string) {
this.id = id;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
}
const userObj = {
id: 123,
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Cage",
extraProperty: 123,
};
const userInstance = plainToInstance(User, userObj, {
excludeExtraneousValues: true,
groups: ["admin"],
});
|
userInstance 返回结果:

4.2 @Exclude()
用于标记属性来在转换后排除它们
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| import { Exclude, plainToInstance } from "class-transformer";
class User {
id: number;
@Exclude()
firstName: string;
@Exclude({ toPlainOnly: true })
lastName: string;
constructor(id: number, firstName: string, lastName: string) {
this.id = id;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
}
const userObj = {
id: 123,
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Cage",
};
const userInstance = plainToInstance(User, userObj);
|
userInstance 输出结果:
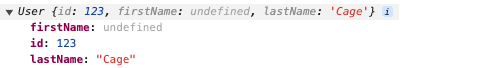
自定义一个函数来转换值,用来指定如何处理这个属性的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import { Transfrom, plainToInstance } from "class-transformer";
class User {
firstName: string;
@Transform((obj) => {
return obj.value + "123";
})
lastName: string;
constructor(firstName: string, lastName: string) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
}
const userObj = {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Cage",
};
const userInstance = plainToInstance(User, userObj);
|
userInstance 输出结果:

@Transform 中转换函数接收的对象参数,包括以下属性:
- key:当前属性的名称
- obj:包含当前属性的整个对象
- options:当前操作的选项配置
- type: 转换操作类型
- value:当前属性的值

4.4 @Type()
指定类的属性在转换时应该的目标类型,主要用于复杂类型的转换场景
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| import { Transfrom, Type, plainToInstance } from "class-transformer";
class Address {
street: string;
@Transform(({ value }) => {
return value.toUpperCase();
})
city: string;
constructor(street: string, city: string) {
this.street = street;
this.city = city;
}
}
class User {
id: number;
@Type(() => Address)
address: Address;
constructor(id: number, address: any) {
this.id = id;
this.address = address;
}
}
const userObj = {
id: 1,
address: {
street: "123 Main St",
city: "shanghai",
},
};
const userInstance = plainToInstance(User, userObj);
|
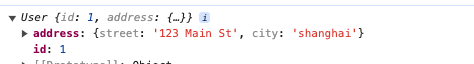
userInstane 输出结果:

如果不增加 @Type 装饰器则会输出:
- 场景 1:
- service 中使用,处理接口返回的数据,比如枚举映射、时间格式处理等
- class 的定义放到 entity 中
- 场景 2:
- service 中使用,处理接口需要的参数,比如补充参数默认值等
- class 的定义放到 dto 中
6. 配合 class-validator
6.1 什么是 class-validator
文档:https://github.com/typestack/class-validator
class-validator 可以为类的属性添加校验,确保类实例的属性值满足特定约束。一般配合 class-transformer 使用
6.2 使用场景
Controller 层,定义 Dto,代表这个 post 请求传入的数据结构。虽然 User 类定义了每个属性的类型,但其实是可以传入任意类型的,比如 id 传入 String 类型也是不会有任何报错
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import { Body, Controller, Post } from "@nestjs/common";
class UserDto {
id: number;
email: string;
constructor(id: number, email: string) {
this.id = id;
this.email = email;
}
}
@Controller("/query")
export class UserController {
@Post("/userInfo")
queryUserInfo(@Body() userDto: UserDto): string {
const response = `User Info - ID: ${userDto.id}, Email: ${userDto.email}`;
return response;
}
}
|
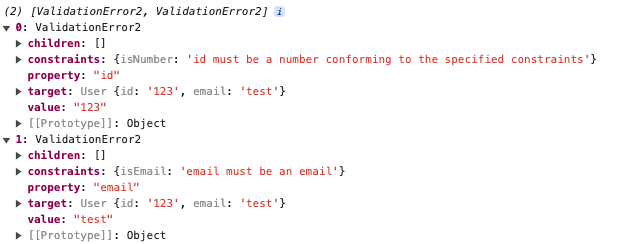
通过 class-validator 对数据类型进行校验
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| import { Body, Controller, Post } from "@nestjs/common";
import { plainToInstance } from "class-transformer";
import { IsNumber, IsEmail, validate } from "class-validator";
class UserDto {
@IsNumber()
id: number;
@IsEmail()
email: string;
constructor(id: number, email: string) {
this.id = id;
this.email = email;
}
}
@Controller("/query")
export class UserController {
@Post("/userInfo")
async queryUserInfo(@Body() userDto: UserDto): string {
const userInstance = plainToInstance(UserDto, userDto);
const errors = await validate(userInstance);
if (errors.length > 0) {
throw new HttpException(
{
status: HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST,
error: "Validation failed",
message: errors.map((error) => error.constraints),
},
HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST
);
}
const response = `User Info - ID: ${userDto.id}, Email: ${userDto.email}`;
return response;
}
}
|
errros 返回内容:
6.3 结合 ValidationPipe 管道
ValidationPipie 是@nestjs/common 提供的,能够利用 class-validator 提供的装饰器进行自动验证,并且使用 class-transformer 来转换请求体中的普通对象为 DTO 的类实例。使得在 Nest 中处理和验证传入数据变得简单且一致
使用 ValidationPipe 改写 queryUserInfo 方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import {
Body,
ValidationPipe,
Controller,
Post,
UsePipes,
} from "@nestjs/common";
import { IsNumber, IsEmail } from "class-validator";
class UserDto {
@IsNumber()
id: number;
@IsEmail()
email: string;
constructor(id: number, email: string) {
this.id = id;
this.email = email;
}
}
@Controller("/query")
export class UserController {
@Post("/userInfo")
@UsePipes(new ValidationPipe())
async queryUserInfo(@Body() userDto: UserDto): string {
const response = `User Info - ID: ${userDto.id}, Email: ${userDto.email}`;
return response;
}
}
|
6.4 常用装饰器
更多:https://github.com/typestack/class-validator
| 类型 | 装饰器 | 含义 |
|---|
| 通用验证 | @IsEmpty() | 检查给定值是否为空(=== ‘’, === null, === undefined) |
| @Equals(comparison: any) | 检查值是否相等(“===”) |
| @IsIn(values: any[]) | 检查值是否在允许值的数组中 |
| 类型验证 | @IsInt() | 是否为整数 |
| @IsDate() | 是否为日期 |
| @IsString() | 是否为字符串 |
| 数字验证 | @IsPositive() | 是否是大于 0 的整数 |
| @Min(min: number)td> | 是否大于等于给定的数字 |
| 字符串验证 | @Contains(seed: string) | 是否包含指定的子字符串 |
| @IsBase64() | 是否是 base64 编码 |





















