Redux(重点)
1、简介
2013年Facebook提出了Flux架构的思想,引发了很多的实现。2015年,Redux出现,将Flux与函数式编程结合一起,很短时间内就成为了最热门的前端架构。
纯函数:输出完成有输入决定的函数
函数的副作用(side effect):发请求,dom操作,…..
简单说,如果你的UI层非常简单,没有很多互动,Redux就是不必要的,用了反而增加复杂性。
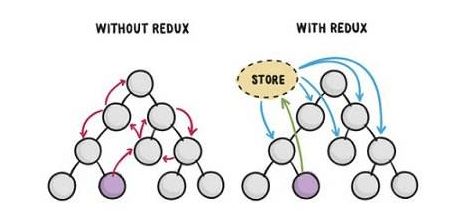
如果你的项目的迭代变得越来越复杂,组件的数量和层级也变得越来越多,越来越深,此时组件间的数据通信就变得异常的复杂和低效,为了解决这个问题,引入了状态管理(redux)从而很好的解决多组件之间的通信问题。
如果需要使用Redux请先进行安装:
网址:https://redux.js.org/introduction/getting-started
作用:项目进行大规模数据管理的工具。
提醒:所有的代码需要从0开始写(不像vuex,选择了vuex后会自带一些代码)
2、三大原则(重点)
纯函数是函数式编程的概念,必须遵守以下一些约束。
请注意:由于reducer被要求是纯函数,所以reducer函数里面不能改变State,必须返回一个全新的数据(不会自动合并原始数据的,因此一定要注意:别把原始数据搞丢了)。
操作原理图
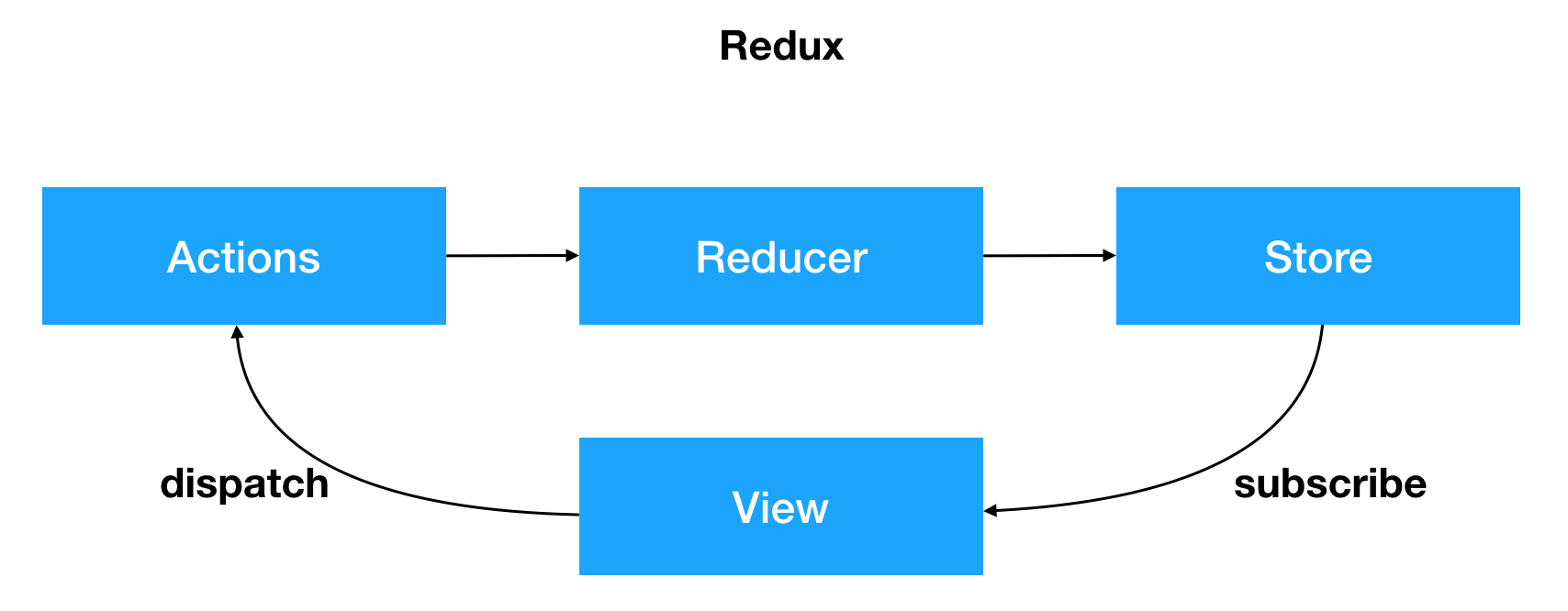
a. store通过reducer创建了初始状态
b. view通过store.getState() 获取到了store中保存的state挂载在了自己的状态上
c. 用户产生了操作(事件),调用了actions 的方法
d. actions的方法被调用,创建了带有标示性信息的action(描述对象,描述如何修改数据)
e. store.dispatch方法发送actions任务到了reducer中
f. reducer接收到action并根据标识信息判断之后返回了新的state(自己注意合并的问题)
g. store的state被reducer更改为新state的时候,store.subscribe方法里的回调函数会执行,此时就可以通知view去重新获取state
- store.getState():用于获取仓库中初始的数据(一次性)
- store.dispatch():用于派发修改数据的任务,参数是action普通对象
- store.subscribe(callback):视图组件用于订阅新数据的方法(二次及以后的数据更新,使之产生类似于vue的响应式store数据)
3、redux的基本使用(存。取,改)
案例:在组件中展示一个按钮,点按钮后给redux中的数字+9,数字初始为0。实现一个计数器的效果
步骤:
- 创建store
- 创建视图组件(展示store中的数据)
- 修改
- 回显数据到视图组件
实现步骤
a. 创建默认数据源:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
import { createStore } from "redux";
const defaultState = {
count: 0,
num:100
};
function reducer(state = defaultState, actions) {
if (actions.type === '+') {
return {
...state,
count: state.count + actions.payload
}
}
return state;
}
const store = createStore(reducer);
export default store;
|
为了方便调试redux(可选安装),建议去谷歌商店安装redux devtools(或到插件迷网站下载),在使用的时候需要参考其说明页面
redux工具条在安装好之后不能直接使用,需要配置仓库代码,然后才能使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
const store = createStore(
reducer,
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
);
|
显示效果:

b. 建立视图组件并且展示数据源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| import React, { Component } from "react";
// 需要导入store;
import store from "../store/index";
class Counter extends Component {
// 在constructor中获取store中的数据
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// 获取store数据(一次性,不具备响应式)
this.state = store.getState();
// 重新订阅store中的数据更新state, 每次修改store中的数据都会触发该方法
// 非简写方式01:
store.subscribe(() => {
//console.log('subscribe');
this.setState(() => {
return store.getState()
})
})
// 简写方式02:
store.subscribe(() => this.setState(() => store.getState()));
}
render() {
console.log(this.state);
return (
<div>
<div>当前Store中的数据是:{this.state.count}</div>
<button onClick={this.addCount.bind(this)}>点击+9</button>
<hr />
<div>当前Store中的数据是:{this.state.age}</div>
<button onClick={this.addAge.bind(this)}>点击+1</button>
</div>
);
}
// 点击+9
addCount() {
// 描述数据如何更改的对象,其必须有type属性
let action = { type: "mod_count", payload: 9 };
// 通过store.dispatch去派发actionr任务(会将该action派发给所有的reducer也就是调用reducer方 法,每个reducer都接收action任务,然后判断执行,因此一定要注意type的取值)
store.dispatch(action);
}
// 点击+1
addAge() {
let action = { type: "mod_age", payload: 1 };
store.dispatch(action);
}
}
export default Counter;
|
c. 修改操作
视图组件中的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| handler() {
const action = {
type: "add",
payload: 9,
};
store.dispatch(action);
}
|
仓库文件的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| function reducer(state = defaultState, actions) {
console.log(actions);
if (actions.type === "add") {
return {
...state,
count: state.count + actions.payload
};
}
return state;
}
|
d. 回显新的数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = store.getState();
store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState(() => store.getState());
});
}
|
f. 当处理多个reducer 方法时,由于不同的reducer 操作的是不同模块的数据,所以需要单独维护
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
import { legacy_createStore as createStore, combineReducers } from 'redux';
const defaultState = {
count: 0,
num: 100
}
function reducer(state = defaultState, actions) {
if (actions.type == '+') {
return {
...state,
count: state.count + actions.payload
}
}
return state
}
function reducer1(state = defaultState, actions) {
if (actions.type == 'jia') {
return {
...state,
num: state.num + actions.payload
}
}
return state
}
const store = createStore(combineReducers({ reducer, reducer1 }), window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__());
export default store
|
f1. 多个reduce在页面中显示数据并操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import React, { Component } from 'react';
import store from '../../store';
console.log(store);
class Test extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = store.getState();
console.log(this.state);
store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState(() => {
return store.getState()
})
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
我是test 组件
<p>{this.state.reducer.count}<button onClick={this.addCount}>+1</button></p>
<p>{this.state.reducer1.num}<button onClick={this.addNum}>+10</button></p>
</div>
);
}
addCount = () => {
store.dispatch({ type: '+', payload: 1 })
}
addNum = () => {
store.dispatch({ type: 'jia', payload: 10 })
}
}
export default Test;
|
4、react-redux(便于全局使用)
网址:https://react-redux.js.org/
React-Redux是Redux的官方针对React开发的扩展库,默认没有在React项目中安装,需要手动来安装。react-redux是依赖于redux,所以必须先安装redux。
我们可以理解为react-redux就是redux给我们提供的高阶组件加工厂。
使用react-redux 可以很方便我们去操作redux
React-redux所能解决的问题是:
每个组件使用仓库的时候,需要 import store from ‘路径’ ,仓库store没有实现全局化(而vue在每个组件可以直接访问全局数据,无需导入 this.$store.state)
使用它以后我们不需要在每个组件中再去 手动订阅数据的更新了store.subscribe(…)(vue不需要) 。
this.state=store.getState() 已经占用了数据的初始化state赋值,当前组件自身state的数据无法额外添加,
为了解决上述问题. 使用本节的react-redux, 但该方法并不是为了简化代码的,它们存在的意义是解决前面所遇到的问题
使用步骤
在项目入口文件中定义Provider
该步骤的操作有点类似于之前组件通信中的context那块的操作
将整个仓库作为商品提供给App根组件,后续的所有的组件都可以获取到仓库store中的数据
注意:与context不一样,这里绑定数据使用的属性是“store”
入口 index.js 文件中的示例代码:
// 导入
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
// 导入provider
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import store from "./store/index";
// 导入需要展示的组件
import App from "./Login";
// 渲染视图
// 在展示app组件的时候需要按照组件的形式进行操作
ReactDOM.render(
//使用Provider组件包裹,将要共享的数据设置为store属性,这个每个后代组件都能获取到该store数据了
// 此时 store 数据就实现了全局化了
<Provider store={store}>
<App></App>
</Provider>,
document.getElementById("root")
);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
- 在需要使用redux的组件中使用
- 这个步骤与vuex中map系列函数(mapState,mapMutations,mapActions、mapGetters)的思想是一样的
- 思想:将仓库中的属性和方法映射成当前组件自身的属性和方法
- 在实际使用的时候组件中不再需要使用store对象了(包括初始的获取数据:store.getState()、store.dispatch()、store.subscribe())
- 步骤
- 在需要使用redux的组件前面导入react-redux提供的高阶组件:connect
- 编写映射方法(请注意,这个方法映射不是类组件的方法,而是在类组件外写的方法)
- mapStateToProps(state)
- 作用:将仓库中的state数据源映射成本组件的属性props,返回一个props对象
- 参数:仓库中的state
- mapDispatchToProps(dispatch)
- 作用:将派发action的方法映射成当前组件自身的属性,该方法也要求返回一个对象,该对象中存放的就是派发action的方法集合
- 参数:dispatch如同之前的store.dispatch()
- 编写时,可以写箭头函数,也可以写常规函数
- 应用高阶组件connect,写法是固定的 connect(参数1,参数2)(组件名)
- ~~~js
// 在组件最后导出的时候改写成如下:
// 从react-redux 导入的connect 参数1,参数2 固定的
// 参数1为mapStateToProps 函数,且该函数必须返回一个对象,否则报错
// 参数2为mapDispatchToProps 函数, 且该函数必须返回一个对象,否则报错
export default connect(mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToProps)(ComponentName)
|
组件中实际使用时的参考代码:以jsx为例
import React, { Component } from "react";
// 第一步:在需要使用redux组件中导入一个由react-redux提供的hoc
import { connect } from "react-redux";
class Counter extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>当前Store中的数据是:{this.props.tool.count}</div>
<button onClick={this.props.addCount}>点击+9</button>
<hr />
<div>当前Store中的数据是:{this.props.user.age}</div>
<button onClick={this.props.addAge}>点击+1</button>
</div>
);
}
}
// 第二步:在类外面定义俩个映射方法
// 将redux中的state数据源属性映射到本组件自身的props属性中
function mapStateToProps(state) {
// return state.user;
// return state.tool;
return state;
}
// 将修改数据的方法dispatch映射成自身组件的props属性
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
// 该方法返回一个对象,对象中都是方法
return {
addCount() {
dispatch({type:'+',payload:1});
},
addAge() {
dispatch({type:'jia',payload:2});
},
};
}
// 第三步:应用HOC
// connect函数的俩个参数顺序不能颠倒
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Counter);
1
2
3
4
5
|
connect写法是传统写法
useSelector 拿到仓库里的数据
|
let state= useSelector(state=>state); 参数是回调,直接可以拿到仓库里的数据
1
2
3
4
5
|
useDispatch 就直接可以抛发动作
|
let dispatch=useDispatch(); dispatch(动作对象)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
|
## 5、Redux模块化
> 如果redux需要使用多个模块,请使用combineReducers方法将多个reudcer函数进行组合,得到一个根reducer对象,将对象传递给创建仓库的方法:https://redux.js.org/tutorials/fundamentals/part-3-state-actions-reducers#combinereducers
针对redux的模块化,在一个常规项目中会将其代码拆分成以下几个部分:
- Reducers,建立同名目录,存放模块化之后的reducer
- types : 建立同名目录,存放types (这样可以集中管理type)
具体实现,以项目的代码为准。
```jsx
//store 目录下的index.js
// 1.导入createStore 方法 用它来创建store
import { createStore, combineReducers } from 'redux';
// 2. 创建一个默认数据对象, 可以定义多个数据
const defaultState = {
count: 0, // 该数据为user模块中的数据
num: 100 // 该数据为shoppingCar模块中的数据
}
// dispatch派发一个actions时,所有的reducer方法都被执行,所以reducer中的type值都不一样
//3. 创建 user模块的 reducer 纯函数, 返回state 对象
function user(state = defaultState, actions) {
// 此处可以操作state中的数据,
if (actions.type === '+') {
return {
...state,
count: state.count + actions.payload
}
}
if (actions.type === '-') {
//console.log(3, state.count, actions.payload)
return {
...state,
count: state.count - actions.payload
}
}
return state
}
//4. 创建shoppingCar模块的reducer纯函数,返回state 对象
function shoppingCar(state = defaultState, actions) {
if (actions.type === 'add') {
return {
...state,
num: state.num + actions.payload
}
}
return state
}
// 5. 使用combineReducers 可以将多有的reducer方法进行合并,参数为对象,对象的key为模块的名称
// 有点类似于vuex的命名空间
const reducers = combineReducers({ user: user, shoppingCar: shoppingCar })
// 6. 创建仓库
const store = createStore(reducers, window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__())
// 7. 导出仓库
export default store
```
```jsx
// 页面操作部分
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
class Thirteenclass extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>测试redux</h1>
<p>store中的数据count: {this.props.user.count}</p>
<p>
<button onClick={this.props.addFn}>+1</button>
</p>
<hr />
<p>store中的数据num: {this.props.shoppingCar.num}</p>
<p>
<button onClick={this.props.addNum}>+1</button>
</p>
</div>
);
}
}
// 将state 映射成自身组件的props
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return state
}
// 将dispatch映射成自身组件的props
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
return {
addFn() {
// 同步调用
//dispatch({ type: '+', payload: 1 })
// 异步调用 如下:payload的值为接口返回的数据,不是固定的值(该接口返回一个随机数)
fetch('https://api.i-lynn.cn/rand').then(res => res.json()).then(res => {
dispatch({ type: '+', payload: res.payload })
})
},
addNum() {
dispatch({ type: 'add', payload: 1 })
}
}
}
// 应用高阶组件connect,写法是固定的 connect(mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToProps)(组件名)
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Thirteenclass);
```
模块化目录及文件内容实例:
~~~js
//第一步: 拆分types, store目录下/types/index.js(这样便于集中化管理
const types = {
addCount: '+',
addNum: 'add'
}
export default types
// 第二步: 拆分 reducers, store目录下/reducers/ 不同的模块创建不同的js并导出该函数
#reducers目录
#user.js文件
import types from "../types/types"
const defaultState = {
count: 0,
num: 100
}
//创建reducer 纯函数, 返回state 对象,
function user(state = defaultState, actions) {
// 此处可以操作state中的数据
if (actions.type === types.addCount) {
return {
...state,
count: state.count + actions.payload
}
}
return state
}
export default user
#shoppingCar.js文件
// 代码同user.js
|
面试题:如果项目有100甚至更多个reducer模块,后续就得import100次甚至更多次,虽然代码简单,但是很繁琐,请问如何优化?
如下这种情况:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
import user from './reducers/user'
import shoppingCar from './reducers/shoppingCar'
import ... from '路径'
const reducers = combineReducers({ user: user, shoppingCar: shoppingCar,... })
const store = createStore(reducers, window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__())
|
将上述写法优化如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
const files = require.context('./reducers/', false, /\.js$/)
console.log(files.keys())
const result = {}
files.keys().forEach(item => {
const start = item.lastIndexOf('/')
const end = item.lastIndexOf('.')
const name = item.substring(start + 1, end)
const val = files(item).default
result[name] = val
});
const reducers = combineReducers(result)
const store = createStore(reducers, window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__())
export default store
|