Nestjs简介
Nestjs 简介
框架简介
- 介绍
用于高效、可扩展的 Node.js 服务端应用程序的框架,使用渐进式 Javascript,结合了面向对象(OOP)、函数式编程(FP)、函数响应式编程(FRP)思想。 - 理念
开箱即用,创建高度可测试、可扩展、松耦合且易于维护的应用程序。
OOP:
使用 Class 作为主要代码组织单元,主要使用@Injectable 标记为可注入依赖项,通过依赖注入的方式实现控制反转,达到类之间的松耦合;
通过继承扩展基类来创建具体的子类实现更具体的功能,比如自定义异常可以继承标准 HTTPException 进行扩展;FP:
针对无依赖项的中间件,我们可以使用纯函数中间件实现;FRP:
Controller 除了返回 Promise 对象,还可以返回 Observable 对象,其能力由 RxJS 库提供,可以监听事件或者数据源进行最终数据的返回;
Nestjs vs Express、Fastify
- TypeScript 支持(Fastify 是原生支持 TS)
- 依赖注入,简化实例的创建与管理
- 模块化架构,按功能拆分模块,分界清晰
- 元数据反射,可以使用装饰器实现路由、守卫等定义,并且可以解析元数据中包含的信息
- 内置模块和功能,路由、HTTP 模块、异常处理等内置功能,更轻松的构建应用
- HTTP 服务器适配,低代价切换 express 与 fastify
- 可插拔插件系统,通过第三方与自定义插件,渐进式扩展应用
模块
- @Module 装饰器修饰的类;
- Nestjs 组织应用程序结构的基本单元;
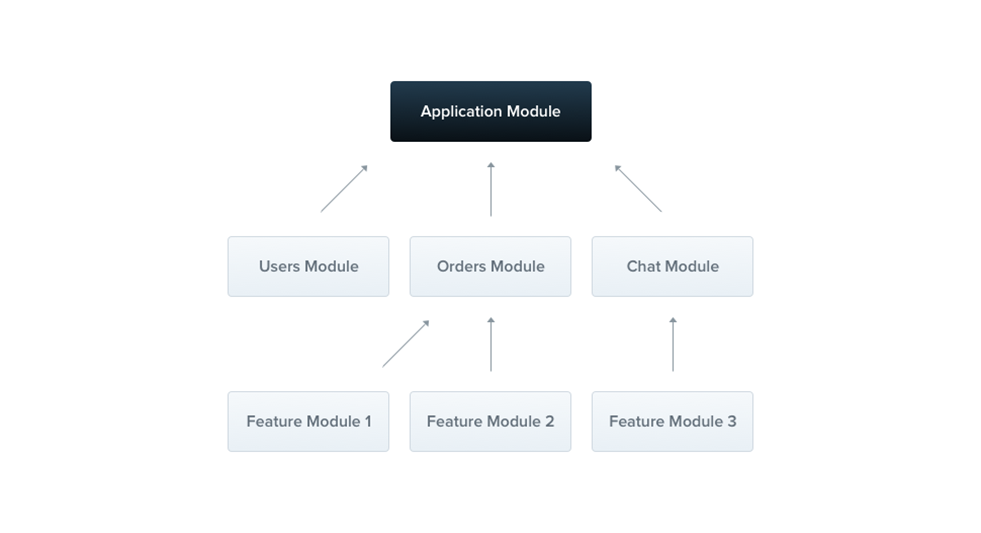
每个应用程序至少有一个根模块,应当将模块作为组织代码的有效方式,最终程序将会包含多个模块,每个模块封装一组密切相关的功能。
1 | // Module |
- providers:模块内可以被 nestjs 注入的提供者
- controllers:模块控制器
- imports:导入模块列表,可以使用导入模块中导出的提供者,如果一个模块被所有模块使用,那么可以@Global 装饰器标记为全局模块
- exports:导出模块或者提供者,供外部模块使用
Providers
通过@Injectable 装饰器修饰,可以在构造函数中声明注入;
1 | // Module |
1 | // Module |
基础概念
模块作为组织代码的基础单元,需要搭配 Nestjs 内置的功能组件来完成一个完整的 HTTP 请求,其中包括:
- 中间件(Middleware)
- 守卫(Guard)
- 拦截器(Interceptor)
- 管道(Pipe)
- 异常过滤器(ExceptionFilter)
中间件
创建
路由处理程序之前调用,可以访问请求和响应对象,调用 next()将控制权交由下一个中间件。
1 | // Middleware |
应用
- 包含中间件的模块必须实现 NestModule 接口;
- 通过 MiddlewareConsumer 控制中间件应用范围;
1 | // Middleware |
多个中间件配置可以通过 consumer 的多次调用进行配置,如果生效路由一致,也可以在 apply 方法中传递多个中间件
全局中间件可以在程序入口中使用 app.use 进行注册
函数式中间件
逻辑简单,无成员、附加方法,无依赖项。
1 | // Middleware |
使用场景
- 认证和授权:验证用户身份、角色、权限,针对特定路由进行访问控制;
- 日志记录:记录请求时间、IP 地址、用户信息等公共基础日志;
- 数据转换:比如 cookie 结构化数据转换等;
守卫
创建
职责单一,负责授权
1 | // Guard |
应用
全局绑定
1
2
3// Guard
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalGuards(new RolesGuard());控制器绑定
1
2
3
4// Guard
("cats")
(RolesGuard)
export class CatsController {}useGlobalGuards 绑定的全局守卫无法注入依赖;
1
2
3
4
5// Guard
({
providers: [provide: APP_GUARD, useClass: RolesGuard, ],
})
export class AppModule {}useGlobalGuards 因为在模块上下文环境之外,无法完成依赖注入;
通过在跟路由中配置 provider 的方式实现全局守卫的注册解决这个问题;拦截器、管道、异常过滤器都可以通过这种方式解决全局注册问题;
使用场景
中间件鉴权 vs 守卫鉴权
守卫中可以获取当前执行上下文,明确知道接下来需要执行的内容;
1 | // Guard |
1 | // Guard |
守卫可以通过执行上下文获取更为详细的信息,针对特定路由进行更为负责的鉴权逻辑;
拦截器
创建
- 路由方法执行前/后绑定额外的逻辑;
- 转换函数返回结果;
- 扩展基本功能;
1 | // Interceptor |
应用
全局绑定
1
2
3// Interceptor
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGLobaLInterceptors(new LoggingInterceptor());控制器绑定
1
2
3// Interceptor
(LoggingInterceptor)
export class CatsController {}
拦截器全局绑定也会有无法注入依赖的问题与守卫处理方式相同;
使用场景
- 路由处理时间;
- 响应数据统一处理;
- 异常映射;
- 缓存覆盖;
异常映射:根据不同的错误映射到不同的异常类型;
缓存覆盖:命中缓存之后,跳过路由逻辑,直接返回数据结果;
管道
创建
- 转换:将输入数据转换为需要形式;
- 验证:校验输入数据是否有效;
1 | // Pipe |
转换管道
- ParseIntPipe
- ParseFloatPipe
- Parse*Pipe
1 | // Pipe |
1 | // Pipe |
校验管道
- ValidationPipe:结合 class-validator、class-transformer 通过装饰器对 Class / DTO 进行校验。
1 | // Pipe |
1 | Pipe; |
应用
全局注册,以便于所有传入 DTO 都需要进行校验;
1
2
3
4
5
6// Pipe
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGLobalPipes(new ValidationPipe());
await app.listen(3000);
}路由注册,针对指定路由进行参数校验与转换;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// Pipe
()
async findALL(
('activeOnLy', new DefaultValuePipe(false), ParseBooLPipe) activeonLy: boolean,
('page', new DefaultVaLuePipe(0), ParseIntPipe) page: number, ) {
return this.catsService.findALL({
activeonly,
page
});
}
异常过滤器
创建
负责程序中未处理异常捕获,返回用户友好响应;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15// Exception
(HttpException)
export class HttpExceptionFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: HttpException, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<Response>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const status = exception.getstatus();
response.status(status).json({
statusCode: status,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: request.url,
});
}
}
自定义异常
- 内置异常
- NotFoundException
- UnauthorizedException
- …
- 自定义异常
1
2
3
4
5
6// Exception
export class ForbiddenException extends HttpException {
constructor() {
super("Forbidden", HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN);
}
}
应用
全局绑定
1
2
3
4
5
6
7// Exception
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGLobaLFilters(new HttpExceptionFilter());
await app.listen(3000);
bootstrap();
}局部绑定
1
2
3// Exception
(new HttpExceptionFilter())
export class CatsController {}
请求生命周期
- 传入请求
- 全局中间件->模块中间件
- 全局守卫->控制器守卫->路由守卫
- 全局拦截器->控制器拦截器->路由拦截器
- 全局管道->控制器管道->路由管道->路由参数管道
- 控制器逻辑->Service->Dao
- 路由拦截器->控制器拦截器->全局拦截器
- 路由异常过滤器->控制器异常过滤器->全局异常过滤器
- 返回响应
Fastify vs Express
- 更高的性能;
- 异步支持;
- 低内存低 CPU;
- 原生 Typescript 支持;
Fasity 在设计时着重优化了性能方面,使用更为高效的路由匹配算法、更为快速的内置 JSON 解析器,内部全异步实现,所以具备更好的性能;
内置支持 async\await 异步处理,区别与 express 的回调方式,可以更高的组织代码和更为高效;
Fasity 精简核心库具备更小的体积,优化了数据结构和算法降低内存的使用,基于事件驱动,减少阻塞从而提高 CPU 的利用率;
模块内部数据流转
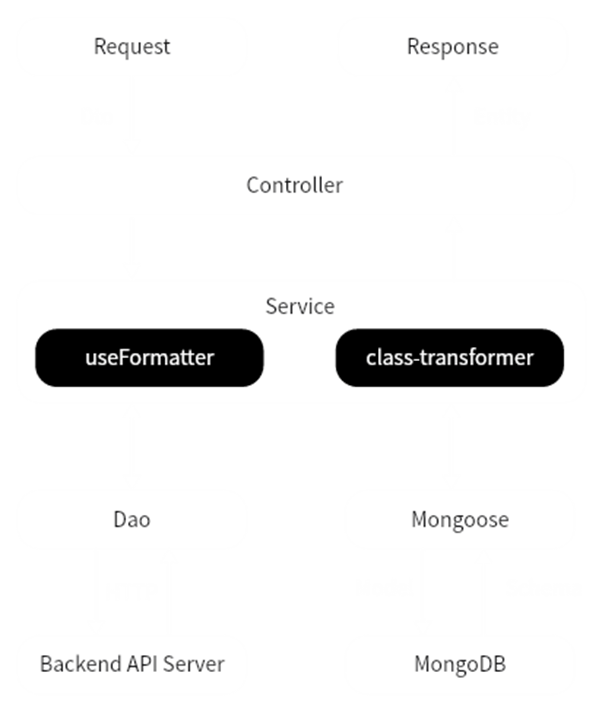
class-transformer
- Plain to Class
- 过滤属性
- 类型嵌套
- 设置别名
- 数据转换
Features
- 请求数据校验
- 接口缓存
- 拦截器统一返回数据
- 异常映射分类
- ……