ajax
一、ajax介绍
工作中的项目都是前后端分离模式进行开发的,前端渲染页面需要的数据是跟后端请求回来的。前端对后端发送请求,除了使用a标签、输入网站敲回车、引入css、引入js、引入网站图标、引入图片,表单之外,还可以使用另外一个技术ajax。
为什么有了其他请求方式,还需要ajax?
- a标签跳转页面,只能发送get请求,无法发送post方式,且无法设置请求头
- 输入网址敲回车,只能发送get请求,无法发送post方式,且无法设置请求头
- 引入css,只能发送get请求,无法发送post方式,且无法设置请求头,请求回来的数据只能被解析成css
- 引入js,只能发送get请求,无法发送post方式,且无法设置请求头,请求回来的数据只能被解析成js代码
- 引入网站图标,只能发送get请求,无法发送post方式,且无法设置请求头,请求回来的数据只能被解析成网站图标
- 引入图片,只能发送get请求,无法发送post方式,且无法设置请求头,请求回来的数据只能被解析成图片
- 表单提交,可以发送get请求,可以发送post请求,但无法设置请求头,且请求发送依赖页面跳转,页面不跳转就无法发送请求
- ajax,可以发送get请求,可以发送post请求,可以设置请求头,请求发送不依赖页面跳转,页面不跳转也可以发送请求
ajax技术在项目中应用广泛,且每个项目必须用到ajax来发送请求,例如:三级联动,页面不刷新但数据要重新请求回来。
三级联动演示:

再例如:我们在注册失败的时候,会重新跳转到注册页面,彼时,注册表单中的数据都清空了,可能只会有一个数据不正确,但我们需要重新输入所有的数据,用户体验感不佳。如果能在点击提交的时候,不刷新页面,但也能请求到服务器,用户体验感就好了。
实际应用:
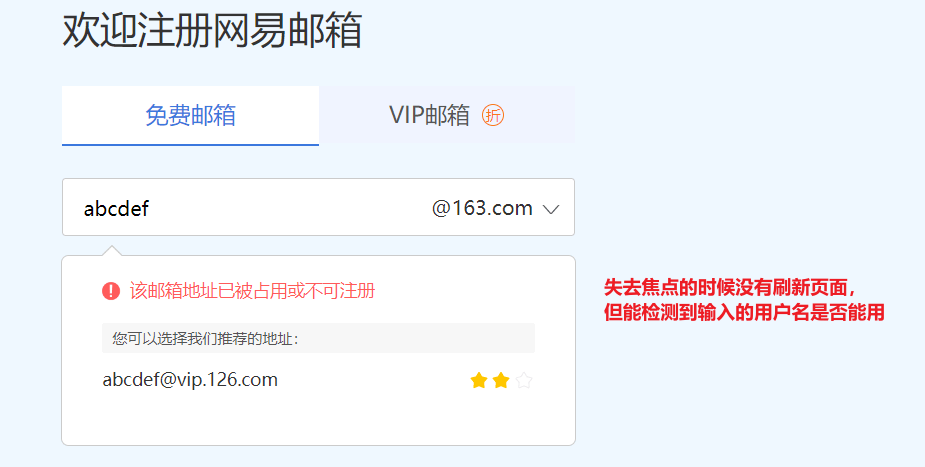
网易邮箱检测用户名是否能用:
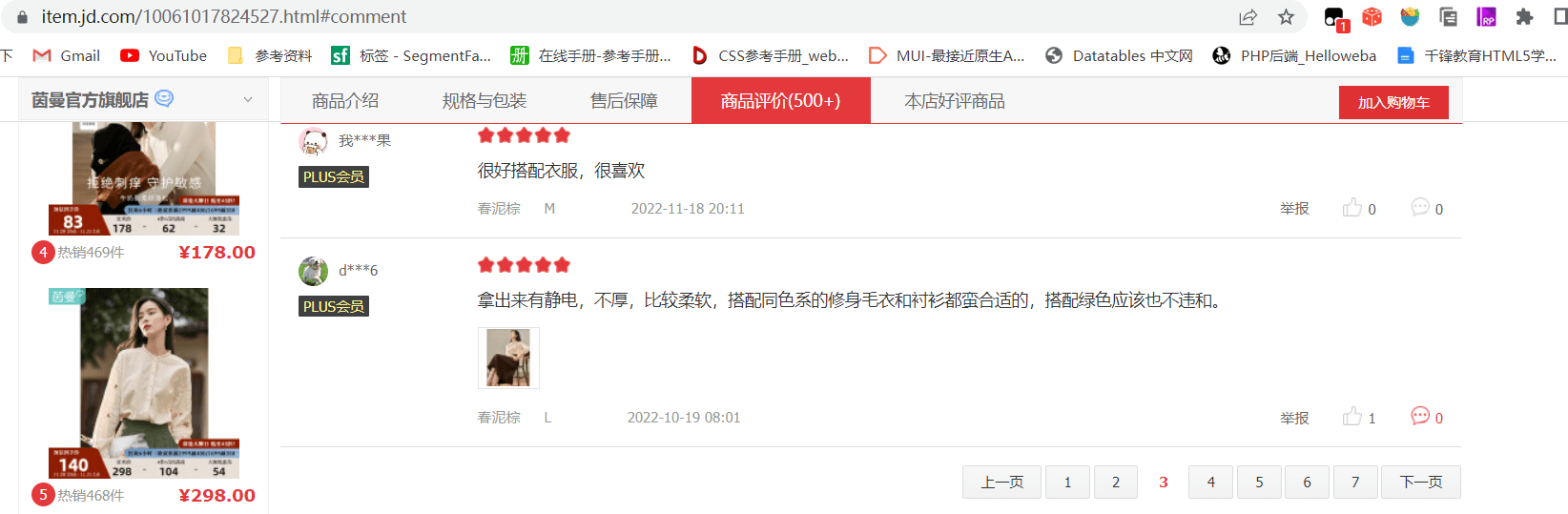
京东商品详情的分页:
二、ajax语法
AJAX,全称:async javascript and XML,是一个异步执行的和后台交互的技术。
创建ajax对象
1
| var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
|
设置请求方式和请求路径
1
| xhr.open(请求方式, 请求地址, true);
|
参数3:是否是异步请求,ajax通常都是异步请求,若要发送同步请求,设置为false,浏览器会有警告。
发送请求
监听请求的状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
xhr.readyState
xhr.status
xhr.responseText
};
|
ajax状态说明:
0:未初始化,对象已经建立,但是还未初始化,就是还未调用open方法
1:请求已经发送,正在发送中
2:请求已经发送服务器
3:服务器正在给客户端响应信息,数据还不完整
4:响应完成,数据全部传送完成,请求结束了
http状态码说明:
1xx:请求发送到服务器了,服务器正在分析这次请求 - 通常指正在请求中
2xx:请求是成功的
3xx:请求收到,但必须要进一步处理 - 通常是准备响应,指定从哪里响应
4xx:客户端错误
5xx:服务器端错误
监听代码说明:
- 判断ajax状态是否完成,要确保数据响应结束
- 响应结束时,判断请求是否是成功的
- 接收响应数据
get请求和post请求不传递参数的情况,上述代码就够了;
post请求传递参数的情况,在上述代码的结束上,需要做些许改动:
在send发送请求之前,必须先设置请求头:
1
| xhr.setRequestHeader('content-type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
|
在send方法中要传递参数:
三、js处理ajax响应的各种数据
1、处理普通字符串
普通字符串接收到后,若要显示在页面中,则使用dom操作;若要进一步处理则使用字符串运算或方法。
例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest;
xhr.open('get','/handlerData');
xhr.send()
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status>=200 && xhr.status<300){
var res = xhr.responseText;
res = res.split('').reverse().join('')
document.querySelector('.box').innerText = res
console.log(res);
}
}
}
|
2、处理json格式字符串
json字符串需要转成数组或对象使用:
例:
后端响应:
1
2
3
4
| res.json({
error_code: 0,
msg: '成功'
})
|
前端处理:
1
2
3
4
5
| res = JSON.parse(res)
let {error_code, msg} = res
if(error_code === 0) {
alert(msg)
}
|
3、处理css字符串
css字符串需要放在style标签中才能生效:
后端响应:
1
| res.end('div{ background: red}')
|
前端处理:
1
2
3
| var style = document.createElement('style')
style.innerText = res
document.head.appendChild(style)
|
4、处理js字符串
返回的数据如果是js代码的字符串,则需要运行js代码:
后端响应:
前端处理:
效果:

5、处理html字符串
需要将响应回来的html字符串,当做某个标签的innerHTML使用:
后端响应:
前端处理:
1
| document.querySelector('.box').innerHTML = res
|
结果:

6、处理xml数据
如果响应的是xml文件数据,则需要通过特殊的属性来接收:
接收到的是一个文档document,可以利用dom操作进行:
xml文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<data>
<student id="1">
<name>张三</name>
<age>12</age>
<sex>男</sex>
</student>
<student id="2">
<name>李四</name>
<age>13</age>
<sex>女</sex>
</student>
</data>
|
xml全称extension markup language,可扩展标记语言,目的是用于存储和传输数据,文件中都是自定义标签。xml文件中不能有xml标签。
后端响应:
1
| res.sendFile(__dirname + '/test.xml')
|
前端处理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| var res = xhr.responseXML
var names = res.querySelectorAll('name')
console.log(names);
for(var a=0; a<names.length; a++) {
console.log( names[a].innerHTML );
}
|
xml的dom中,没有innerText,只有innerHTML
四、ajax处理注册登录
注册html:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>注册</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/register.css">
</head>
<body>
<form action="/user/register" method="post">
<table align="center">
<caption><h2>注册</h2></caption>
<tr>
<td>用户名:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="password"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>确认密码:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="repass"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>邮箱:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="email"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td>
<input type="reset">
<input type="submit">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<div class="container footer">
<div class="content">
已有账号,去<a href="login.html">登录</a>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script src="./js/register.js"></script>
</html>
|
注册js:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| var form = document.querySelector('form')
var usernameInput = document.querySelector('[name="username"]')
var passwordInput = document.querySelector('[name="password"]')
var repassInput = document.querySelector('[name="repass"]')
var emailInput = document.querySelector('[name="email"]')
form.onsubmit = function() {
var usernameReg = /^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]{3,9}$/
if(!usernameReg.test(usernameInput.value)) {
alert('用户名不符合规则')
return false
}
var passwordReg = /^.{6,10}$/
if(!passwordReg.test(passwordInput.value)) {
alert('密码不符合规则')
return false
}
if(passwordInput.value != repassInput.value) {
alert('两次密码输入不一致')
return false
}
var emailReg = /(^[1-9]\d{5,9}@qq\.com$)|(^[a-zA-Z]\w{5,17}@((126|163)\.com|yeah\.net)$)/
if(!emailReg.test(emailInput.value)) {
alert('邮箱不符合规则')
return false
}
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest;
xhr.open('post','/user/register');
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
xhr.send(`username=${usernameInput.value}&password=${passwordInput.value}&email=${emailInput.value}`)
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status>=200 && xhr.status<300){
var res = xhr.responseText;
res = JSON.parse(res)
var {error_code, msg} = res
alert(msg)
if(error_code === 0) {
location.href = '/login.html'
}
console.log(res);
}
}
}
return false
}
|
注册服务器端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
router.post('/register', (req, res) => {
let {username, password, email} = req.body
let data = fs.readFileSync('./data.txt', 'utf-8')
if(data) {
data = JSON.parse(data)
let obj = data.find(item => item.username === username)
if(obj) {
res.json({
error_code: 1,
msg: '用户名被占用'
})
return
}
} else {
data = []
}
data.push({
username,
password: bcryptjs.hashSync(password, 10),
email
})
fs.writeFileSync('./data.txt', JSON.stringify(data))
res.json({
error_code: 0,
msg: '注册成功'
})
})
|
登录html:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/login.css">
</head>
<body>
<form action="/user/login" method="post">
<table align="center">
<caption><h2>登录</h2></caption>
<tr>
<td>用户名:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="password"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td>
<input type="reset">
<input type="submit">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
<script src="./js/login.js"></script>
</html>
|
登录js:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| var form = document.querySelector('form')
var usernameInput = document.querySelector('[name="username"]')
var passwordInput = document.querySelector('[name="password"]')
form.onsubmit = function() {
if(usernameInput.value === '' || passwordInput.value === '') {
alert('账号和密码不能为空')
return false
}
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest;
xhr.open('post','/user/login');
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
xhr.send(`username=${usernameInput.value}&password=${passwordInput.value}`)
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status>=200 && xhr.status<300){
var res = xhr.responseText;
res = JSON.parse(res)
var {error_code, msg} = res
alert(msg)
if(error_code === 0) {
location.href = '/'
}
console.log(res);
}
}
}
return false
}
|
登录服务器端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| router.post('/login', (req, res) => {
let {username, password} = req.body
let data = fs.readFileSync('./data.txt', 'utf-8')
if(!data) {
res.json({
error_code: 1,
msg: '还未注册'
})
return
}
data = JSON.parse(data)
let obj = data.find(item => item.username === username)
if(obj) {
if(bcryptjs.compareSync(password, obj.password)) {
res.json({
error_code: 0,
msg: '登录成功'
})
return
}
res.json({
error_code: 2,
msg: '密码不正确'
})
} else {
res.json({
error_code: 3,
msg: '用户名不存在'
})
}
})
|
五、cookie和本地存储
1、cookie介绍
当登录成功后应该跳转到首页,首页要显示登录过的账号或昵称。但首页显示是又一次http请求,登录是上次的http请求,两次请求之间的状态是无法保持的,所以默认是获取不到登录的账号的。
http请求,每次都有三次握手、通信、四次挥手的过程,所以多次请求之间是完全没有关联的,登录过的状态是无法保持给后续请求的。所以http协议又叫做无状态协议。
但在实际项目中,我们又需要在多次请求之间保持一定的状态,例如,登录过后的所有页面都要保持登录过的状态。这时候就需要用到cookie了。
cookie是基于http无法保持状态而出现的一种解决方案。原理是利用多次请求使用的是同一个浏览器,在浏览器中利用数据的存储来达到保持状态的功能。例如:登录成功后,将账号或昵称保存在浏览器,其他http请求打开页面后,从浏览器中获取数据,判断之前是否登录过。
2、cookie特性
cookie本质上就是http协议下,浏览器的存储技术,有以下几个特性:
- 以键值对形式存储
- 具有时效性,不设置有效期,默认关闭浏览器失效;设置了有效期后,有效期后访问则会自动删除。cookie识别的时间是世界标准时间(东八区时间-8小时)
- 分域名存储,当前域名下设置的cookie,只能在当前域名下访问
- 分路径存储,当前路径下设置的cookie,只能在当前路径下访问
- 大小和数量受浏览器显示,最大4kb,最多150条
- cookie默认会请求头和响应头之间来回传递,也就是默认会带给服务器
3、cookie操作
3.1、存储cookie
1
| document.cookie = 'key=value;expires=失效时间日期对象(世界标准时间);path=路径'
|
一次只能设置一条cookie,设置多条就需要设置多次。
浏览器默认查看cookie的有效期,是使用中国标准时间查看的,所以查看的不准确,需要使用谷歌插件EditCookie进行查看。
3.2、获取cookie
一次性获取到所有的cookie,每个cookie之间使用分号空格分割
3.3、删除cookie
前端js没有删除cookie的语法,可以将cookie的失效时间设置为上1秒,等同于删除cookie。
3.4、cookie操作封装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
function setCookie(key, value, seconds, path = '/') {
var date = new Date()
date.setTime(date.getTime() - 8 * 3600 * 1000 + seconds * 1000)
document.cookie = `${key}=${value};expires=${data};path=${path}`
}
function getCookie(key) {
var cookies = document.cookie
if(!cookies) return
var reg = /[^=; ]=[^; ]/g
while(true) {
var arr = reg.exec(cookies)
if(!arr && arr[1] === key) {
return arr[2]
}
}
}
function removeCookie(key, path = '/') {
setCookie(key, null, -1, path)
}
|
4、本地存储
用户登录后,如果要获取用户详细信息,需要给后端再次发送请求,此时,后端会有需要令牌的验证。
前端登录后,需要将令牌保存起来,后续发送请求需要携带令牌。
通常前端在存储令牌的时候,会将令牌保存在本地存储中。
本地存储也属于浏览器存储数据的一种技术,本地存储由如下几个特点:
- 本地存储是以键值对形式存储的
- 本地存储分域名存储,本地打开的页面也可以存储
- 本地存储没有时效性,默认永久存储
- 本地存储的大小较大一些(5MB)
- 本地存储默认不会携带给服务器
本地存储API:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
window.localStorage.setItem(key, value)
localStorage.getItem(key)
localStorage.removeItem(key)
localStorage.clear()
|
例:存储token
1
| localStorage.setItem('token', token)
|
存储登录后要跳转的路径:
1
| localStorage.setItem('url', location.href)
|
六、ajax封装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
|
function request(obj) {
if(obj.url === undefined) {
throw new Error('请求地址不能为空!')
}
if(typeof obj.url != 'string') {
throw new Error('请求地址不正确!')
}
if(obj.method === undefined) {
obj.method = 'get'
}
if(obj.method.toLowerCase() != 'get' && obj.method.toLowerCase() != 'post') {
throw new Error('请求方式必须是get或post')
}
if(obj.async === undefined) {
obj.async = true
}
if(typeof obj.async != 'boolean') {
throw new Error('async必须是布尔值!')
}
if(obj.data != undefined) {
var data = ''
if({}.toString.call(obj.data) === '[object String]') {
if(!obj.data.includes('=')) {
throw new Error('字符串数据格式:键=值!')
}
data = obj.data
} else if({}.toString.call(obj.data) === '[object Object]') {
var arr = []
for(var key in obj.data) {
arr.push(key + '=' + obj.data[key])
}
data = arr.join('&')
} else {
if(!obj.data.includes('=')) {
throw new Error('数据必须是字符串或独享!')
}
}
if(obj.method.toLowerCase() === 'get') {
obj.url += '?' + data
}
}
if(obj.success === undefined) {
obj.success = () => {}
}
if(typeof obj.success != 'function') {
throw new Error('success必须是函数')
}
if(obj.error === undefined) {
obj.error = () => {}
}
if(typeof obj.error != 'function') {
throw new Error('error必须是函数')
}
if(obj.dataType === undefined) {
obj.dataType = 'json'
}
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest
xhr.open(obj.method, obj.url, obj.async)
if(obj.headers != undefined) {
if({}.toString.call(obj.header) != '[object Object]') {
throw new Error('headers头信息必须是对象!')
}
for(var key in obj.headers) {
xhr.setRequestHeader(key, obj.headers[key])
}
}
if(obj.method.toLowerCase() === 'post' && data != undefined) {
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
xhr.send(data)
} else {
xhr.send()
}
if(obj.async === true) {
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
console.log(xhr.readyState);
if(xhr.readyState === 4) {
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
switch(obj.dataType) {
case 'json':
var res = xhr.responseText
res = JSON.parse(res)
break
case 'text':
var res = xhr.responseText
break
case 'xml':
var res = xhr.responseXML
break
default:
throw new Error('dataType必须是json或text或xml!')
}
obj.success(res)
} else {
obj.error()
}
}
}
} else {
switch(obj.dataType) {
case 'json':
var res = xhr.responseText
res = JSON.parse(res)
break
case 'text':
var res = xhr.responseText
break
case 'xml':
var res = xhr.responseXML
break
default:
throw new Error('dataType必须是json或text或xml!')
}
obj.success(res)
}
}
|
注册:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| request({
method: 'post',
url: '/user/register',
data: {
username: usernameInput.value,
password: passwordInput.value,
email: emailInput.value
},
success(res) {
var {error_code, msg} = res
alert(msg)
if(error_code === 0) {
location.href = '/login.html'
}
}
})
|
登录:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| request({
method: 'post',
url: '/user/login',
data: {
username: usernameInput.value,
password: passwordInput.value
},
success: res => {
var {error_code, msg} = res
alert(msg)
if(error_code === 0) {
location.href = '/'
}
}
})
|
















