《React》课程资料——许小墨
〇、React 一、关于React 英文官网:https://reactjs.org/
中文官网:https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/
React 起源于 Facebook 的内部项目,因为该公司对市场上所有 JavaScript MVC 框架,都不满意,就决定自己写一套,用来架设Instagram 的网站。做出来以后,发现这套东西很好用,就在2013年5月开源了。
react在发展过程中,一直跟随原生js的脚步,特别是从v16.0版本开始(用到了class来创建组件)
2015年推出了使用react来编写移动端的app —- react-native
重要版本发版时间
序号 版本号 发版时间 重要更新 1 16 2017年9月26 引入es6的类组件 2 16.3 2018年4月3日 生命周期更新 3 16.4 2018年5月23日 生命周期更新 4 16.8 2019年2月6日 引入 react hooks 5 17.0 2020年10月20日 过渡版本 6 18.0 2022年3月29日 写法改变,严格模式发生改变
二、脚手架 英文官网:https://create-react-app.dev/
中文官网:https://create-react-app.bootcss.com/
补充:react的脚手架并不是只有 create-react-app,还有dva-cli,umi等
2.1 create-react-app脚手架的使用 Create React App 让你仅通过一行命令,即可构建现代化的 Web 应用。
本文档之后称之为cra
创建项目的方式:
需要保证电脑安装node版本在14以上,系统在win7以上
1 2 3 4 5 6 $ npx create-react-app react-basic $ npm init react-app react-basic $ yarn create react-app react-basic
如果需要使用ts开发项目,创建项目时可以通过--template typescript指定模版
1 $ npx create-react-app myapp --template typescript
如果出现如下内容,即代表项目创建成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Success! Created react-basic at /Users/wudaxun/Desktop/workspace/code/bk2207A/code/react-course/react-basic Inside that directory, you can run several commands: npm start Starts the development server. npm run build Bundles the app into static files for production. npm test Starts the test runner. npm run eject Removes this tool and copies build dependencies, configuration files and scripts into the app directory. If you do this, you can’t go back! We suggest that you begin by typing: cd react-basic npm start Happy hacking!
2.2 项目目录解析 项目创建完毕生成目录结构如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 react-basic ├── README.md ├── node_modules ├── package.json ├── .gitignore ├── public │ ├── favicon.ico │ ├── index.html │ ├── logo192.png │ ├── logo512.png │ ├── manifest.json │ └── robots.txt └── src ├── App.css ├── App.js ├── App.test.js ├── index.css ├── index.js ├── logo.svg ├── reportWebVitals.js // 做性能测试 └── setupTests.js // 测试
src/reportWebVitals.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 const reportWebVitals = onPerfEntry => { if (onPerfEntry && onPerfEntry instanceof Function ) { import ('web-vitals' ).then (({ getCLS, getFID, getFCP, getLCP, getTTFB } ) => { getCLS (onPerfEntry); getFID (onPerfEntry); getFCP (onPerfEntry); getLCP (onPerfEntry); getTTFB (onPerfEntry); }); } }; export default reportWebVitals;
react官方文档已经给了我们性能提升的方案:https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/optimizing-performance.html
打开package.json,发现可运行命令如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 "scripts" : { "start" : "react-scripts start" , "build" : "react-scripts build" , "test" : "react-scripts test" , "eject" : "react-scripts eject" } ,
start指令用于启动开发者服务器
build指令用于打包项目
test指令用于测试
eject指令用于抽离配置文件
cra脚手架基于webpack,默认webpack的配置在 node_modules 下的 react-scripts 内部,但是一般情况下,传输代码时,不会上传 node_modules,那么在必要情况下就必须得抽离配置文件。
2.3 抽离配置文件 通过npm run eject或者cnpm run eject 或者yarn eject指令抽离配置文件
抽离配置文件过程中注意事项
1.确保项目的git仓库是最新的 2.如果不需要对于webpack进行配置,那么不需要抽离配置文件 create-react-app v2 默认支持 ts 以及sass 以及css的模块化,如果使用 sass作为css预处理器,那么不需要抽离配置文件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 Copying files into /Users/wudaxun/Desktop/workspace/code/bk2207A/code/react-course/react-basic Adding /config/env.js to the project Adding /config/getHttpsConfig.js to the project Adding /config/modules.js to the project Adding /config/paths.js to the project Adding /config/webpack.config.js to the project Adding /config/webpackDevServer.config.js to the project Adding /config/jest/babelTransform.js to the project Adding /config/jest/cssTransform.js to the project Adding /config/jest/fileTransform.js to the project Adding /scripts/build.js to the project Adding /scripts/start.js to the project Adding /scripts/test.js to the project Adding /config/webpack/persistentCache/createEnvironmentHash.js to the project Updating the dependencies Removing react-scripts from dependencies Adding @babel/core to dependencies Adding @pmmmwh/react-refresh-webpack-plugin to dependencies Adding @svgr/webpack to dependencies Adding babel-jest to dependencies Adding babel-loader to dependencies Adding babel-plugin-named-asset-import to dependencies Adding babel-preset-react-app to dependencies Adding bfj to dependencies Adding browserslist to dependencies Adding camelcase to dependencies Adding case-sensitive-paths-webpack-plugin to dependencies Adding css-loader to dependencies Adding css-minimizer-webpack-plugin to dependencies Adding dotenv to dependencies Adding dotenv-expand to dependencies Adding eslint to dependencies Adding eslint-config-react-app to dependencies Adding eslint-webpack-plugin to dependencies Adding file-loader to dependencies Adding fs-extra to dependencies Adding html-webpack-plugin to dependencies Adding identity-obj-proxy to dependencies Adding jest to dependencies Adding jest-resolve to dependencies Adding jest-watch-typeahead to dependencies Adding mini-css-extract-plugin to dependencies Adding postcss to dependencies Adding postcss-flexbugs-fixes to dependencies Adding postcss-loader to dependencies Adding postcss-normalize to dependencies Adding postcss-preset-env to dependencies Adding prompts to dependencies Adding react-app-polyfill to dependencies Adding react-dev-utils to dependencies Adding react-refresh to dependencies Adding resolve to dependencies Adding resolve-url-loader to dependencies Adding sass-loader to dependencies Adding semver to dependencies Adding source-map-loader to dependencies Adding style-loader to dependencies Adding tailwindcss to dependencies Adding terser-webpack-plugin to dependencies Adding webpack to dependencies Adding webpack-dev-server to dependencies Adding webpack-manifest-plugin to dependencies Adding workbox-webpack-plugin to dependencies Updating the scripts Replacing "react-scripts start" with "node scripts/start.js" Replacing "react-scripts build" with "node scripts/build.js" Replacing "react-scripts test" with "node scripts/test.js" Configuring package.json Adding Jest configuration Adding Babel preset Running npm install... up to date in 4s 203 packages are looking for funding run `npm fund` for details Ejected successfully!
2.4 webpack二次封装 2.4.1 集成css预处理器 1 $ cnpm i less less-loader -D
1 $ cnpm i stylus stylus-loader -D
具体配置如下:
React-basic/config/webpack.config.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 const cssRegex = /\.css$/ ;const cssModuleRegex = /\.module\.css$/ ;const sassRegex = /\.(scss|sass)$/ ;const sassModuleRegex = /\.module\.(scss|sass)$/ ;const lessRegex = /\.less$/ ;const lessModuleRegex = /\.module\.less$/ ;const stylusRegex = /\.stylus/ ;const stylusModuleRegex = /\.module\.stylus/ ;{ test : cssRegex, exclude : cssModuleRegex, use : getStyleLoaders ({ importLoaders : 1 , sourceMap : isEnvProduction ? shouldUseSourceMap : isEnvDevelopment, modules : { mode : 'icss' , }, }), sideEffects : true , }, { test : cssModuleRegex, use : getStyleLoaders ({ importLoaders : 1 , sourceMap : isEnvProduction ? shouldUseSourceMap : isEnvDevelopment, modules : { mode : 'local' , getLocalIdent : getCSSModuleLocalIdent, }, }), }, { test : sassRegex, exclude : sassModuleRegex, use : getStyleLoaders ( { importLoaders : 3 , sourceMap : isEnvProduction ? shouldUseSourceMap : isEnvDevelopment, modules : { mode : 'icss' , }, }, 'sass-loader' ), sideEffects : true , }, { test : sassModuleRegex, use : getStyleLoaders ( { importLoaders : 3 , sourceMap : isEnvProduction ? shouldUseSourceMap : isEnvDevelopment, modules : { mode : 'local' , getLocalIdent : getCSSModuleLocalIdent, }, }, 'sass-loader' ), }, { test : lessRegex, exclude : lessModuleRegex, use : getStyleLoaders ( { importLoaders : 3 , sourceMap : isEnvProduction ? shouldUseSourceMap : isEnvDevelopment, modules : { mode : 'icss' , }, }, 'less-loader' ), sideEffects : true , }, { test : lessModuleRegex, use : getStyleLoaders ( { importLoaders : 3 , sourceMap : isEnvProduction ? shouldUseSourceMap : isEnvDevelopment, modules : { mode : 'local' , getLocalIdent : getCSSModuleLocalIdent, }, }, 'less-loader' ), }, { test : stylusRegex, exclude : stylusModuleRegex, use : getStyleLoaders ( { importLoaders : 3 , sourceMap : isEnvProduction ? shouldUseSourceMap : isEnvDevelopment, modules : { mode : 'icss' , }, }, 'stylus-loader' ), sideEffects : true , }, { test : stylusModuleRegex, use : getStyleLoaders ( { importLoaders : 3 , sourceMap : isEnvProduction ? shouldUseSourceMap : isEnvDevelopment, modules : { mode : 'local' , getLocalIdent : getCSSModuleLocalIdent, }, }, 'stylus-loader' ), },
2.4.2 配置@解析别名 vue项目中可以使用@代替src目录,那么react中抽离配置文件之后也可以实现此功能
react-basic/config/webpack.config.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 alias : { '@' : path.resolve ('src' ), 'react-native' : 'react-native-web' , ...(isEnvProductionProfile && { 'react-dom$' : 'react-dom/profiling' , 'scheduler/tracing' : 'scheduler/tracing-profiling' , }), ...(modules.webpackAliases || {}), },
如果是ts项目,需要在tsconfig.json中加入如下配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 { "compilerOptions" : { "target" : "es6" , "lib" : [ "dom" , "dom.iterable" , "esnext" ] , "paths" : { "@/*" : [ "./src/*" ] } , "allowJs" : true , "skipLibCheck" : true , "esModuleInterop" : true , "allowSyntheticDefaultImports" : true , "strict" : true , "forceConsistentCasingInFileNames" : true , "noFallthroughCasesInSwitch" : true , "module" : "esnext" , "moduleResolution" : "node" , "resolveJsonModule" : true , "isolatedModules" : true , "noEmit" : true , "jsx" : "react-jsx" } , "include" : [ "src" , "src/**/*" ] }
src/index.js 测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' ;import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' ;import '@/index.css' ; import App from '@/App' ;import reportWebVitals from '@/reportWebVitals' ;const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ));root.render ( <React.StrictMode > <App /> </React.StrictMode > ); reportWebVitals ();
如果控制台报错如下,说明@别名没有配置成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Failed to compile.Module not found : Error : Can 't resolve ' @/index.css ' in ' /Users /wudaxun/Desktop /workspace/code/bk2207A/code/react-course/react-basic/src' ERROR in ./src/index.js 6:0-21 Module not found: Error: Can' t resolve '@/index.css' in '/Users/wudaxun/Desktop/workspace/code/bk2207A/code/react-course/react-basic/src' ERROR in ./src/index.js 7 :0 -24 Module not found : Error : Can 't resolve ' @/App ' in ' /Users /wudaxun/Desktop /workspace/code/bk2207A/code/react-course/react-basic/src' ERROR in ./src/index.js 8:0-48 Module not found: Error: Can' t resolve '@/reportWebVitals' in '/Users/wudaxun/Desktop/workspace/code/bk2207A/code/react-course/react-basic/src' webpack compiled with 3 errors
如果没有错误说明配置是成功的。
如果不抽离配置文件,但是也需要配置别名@
1 $ cnpm i @craco/craco -D
项目根目录中创建 craco 的配置文件:craco.config.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const path = require ('path' )module .exports = { webpack : { alias : { '@' : path.resolve (__dirname, 'src' ) } } }
修改package.json中运行命令
1 2 3 4 5 "scripts" : { "start" : "craco start" , "build" : "craco build" "test" : "craco test" }
重启服务器即可生效
2.5 setupProxy代理 即使不抽离配置文件,也是在此处配置代理
如果整个项目只有一个服务器且有跨域问题,可以直接在package.json中做如下配置:
1 "proxy": "http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/"
然后在项目中可以如下访问:
1 2 3 4 // src/index.js fetch('/pro/list').then(res => res.json()).then(res => { console.log(res.data) })
那么如果有多个服务器 并且也需要解决跨域问题
首先,http-proxy-middleware使用 npm 或 Yarn 安装:
1 2 3 $ cnpm install http-proxy-middleware -S $ $ yarn add http-proxy-middleware -S
接下来,创建src/setupProxy.js并在其中放置以下内容:
1 2 3 4 5 const { createProxyMiddleware } = require ('http-proxy-middleware' );module .exports = function (app ) { };
您现在可以根据需要注册代理了!这是使用上述内容的示例http-proxy-middleware:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const { createProxyMiddleware } = require ('http-proxy-middleware' ); module .exports = function (app ) { app.use ('/myapi' , createProxyMiddleware ({ target : 'http://121.89.205.189:3001/api' , changeOrigin : true , pathRewrite : { '^/myapi' : '' } }) ); }
注意: 您不需要在任何地方导入此文件。当您启动开发服务器时,它会自动注册。
注意: 此文件仅支持 Node 的 JavaScript 语法。确保只使用受支持的语言功能(即不支持 Flow、ES 模块等)。
注意: 将路径传递给代理函数允许您在路径上使用通配符和/或模式匹配,这比快速路由匹配更灵活。
三、JSX 设想如下变量声明:
1 const element = <h1 > Hello, world!</h1 >
这个有趣的标签语法既不是字符串也不是 HTML。
它被称为 JSX,是一个 JavaScript 的语法扩展。
JSX 可以生成 React “元素”。
React 不强制要求 使用 JSX,但是大多数人发现,在 JavaScript 代码中将 JSX 和 UI 放在一起时,会在视觉上有辅助作用。它还可以使 React 显示更多有用的错误和警告消息。
src文件夹下只保留index.js
3.1 jsx语法详解 在下面的例子中,我们声明了一个名为 name 的变量,然后在 JSX 中使用它,并将它包裹在大括号中
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom' const name = <h1 > 千锋HTML5大前端,前端培训界的扛把子!!!!</h1 > const app = <div > 你好, { name }</div > ReactDOM .render ( app, document .getElementById ('root' ) )
在 JSX 语法中,你可以在大括号内放置任何有效的 JavaScript 表达式 。例如,2+2,user.firstName 或 formatName(user) 都是有效的 JavaScript 表达式。
在下面的示例中,我们将调用 JavaScript 函数 formatName(user) 的结果,并将结果嵌入到 <div> 元素中。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' function formatUser (user) { return user.firstName + user.lastName } const user = { firstName : '吴' , lastName : '大勋' } const app = ( <div > 你好, { formatUser(user) } </div > ) const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (app)
jsx也是一个表达式
在编译之后,JSX 表达式会被转为普通 JavaScript 函数调用,并且对其取值后得到 JavaScript 对象。
也就是说,你可以在 if 语句和 for 循环的代码块中使用 JSX,将 JSX 赋值给变量,把 JSX 当作参数传入,以及从函数中返回 JSX
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' function formatUser (user) { return user.firstName + user.lastName } const user = { firstName : '吴' , lastName : '大勋' } function getGreeting (user) { if (user) { return ( <div > 你好, { formatUser(user) } </div > ) } else { return <div > hello error</div > } } const app = getGreeting (user)const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (app)
因为 JSX 语法上更接近 JavaScript 而不是 HTML,所以 React DOM 使用 camelCase(小驼峰命名)来定义属性的名称,而不使用 HTML 属性名称的命名约定。
例如,JSX 里的 class 变成了 classNametabindex 则变为 tabIndex
Babel 会把 JSX 转译成一个名为 React.createElement() 函数调用。
上述代码都没见到使用过 React 模块,但是显示却用了,为什么?
3.2 React.createElement 先看一个代码
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' const app = React .createElement ('div' , { className : 'box' }, 'hello react !!!' )const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (app)
React.createElement() 会预先执行一些检查,以帮助你编写无错代码,但实际上它创建了一个这样的对象:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const element = { type : 'div' , props : { className : 'box' , children : 'hello react' } };
这些对象被称为 “React 元素”。它们描述了你希望在屏幕上看到的内容。React 通过读取这些对象,然后使用它们来构建 DOM 以及保持随时更新。
四、组件定义 组件允许你将 UI 拆分为独立可复用的代码片段,并对每个片段进行独立构思。
组件,从概念上类似于 JavaScript 函数。它接受任意的入参(即 “props”),并返回用于描述页面展示内容的 React 元素。
4.1 类组件 ES6的加入让JavaScript直接支持使用class来定义一个类,react的创建类组件的方式就是使用的类的继承,ES6 class是一种使用React组件的写法,它使用了ES6标准语法来构建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' class App extends React.Component { render () { return ( <div > hello react class component</div > ) } } const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
4.2 函数组件 定义组件最简单的方式就是编写 JavaScript 函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' const App = ( <div > hello react function component </div > ) const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
4.3 两组组件的区别 组件的定义方式不同。 生命周期不同:类组件有,函数式组件没有。 副作用操作执行不同:class组件通过生命周期函数,函数组件用hook的useEffect。 state的定义、读取、修改方式不同:函数组件用hook的useState。 this: class组件有,函数式组件没有。 实例: class组件有,函数时组件没有。 ref使用不同:类组件可以获取子组件实例,函数式组件不可以,因为函数式组件没有实例。 官方推荐使用函数式组件,以上不同点虽然现在不明白是啥意思,没有关系,会随着大家的学习印象加深。
五、Props 5.1 Props详解 props是正常是外部传入的,组件内部也可以通过一些方式来初始化的设置,属性不能被组件自己更改,但是你可以通过父组件主动重新渲染的方式来传入新的 props
React 非常灵活,但它也有一个严格的规则:
所有 React 组件都必须像纯函数一样保护它们的 props 不被更改。
纯函数:输入一定,输出一定确定
总的来说,在使用一个组件的时候,可以把参数放在标签的属性当中,所有的属性都会作为组件 props 对象的键值。
通过箭头函数创建的组件,需要通过函数的参数来接收props
通过类创建的组件,需要通过 this.props来接收
组件可以在其输出中引用其他组件。
这就可以让我们用同一组件来抽象出任意层次的细节。
按钮,表单,对话框,甚至整个屏幕的内容:在 React 应用程序中,这些通常都会以组件的形式表示。
5.2 父子组件通信 5.2.1 构建一个父子组件 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './01_props/01_Parent_Child' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/01_props/01_Parent_Child.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import React from 'react' class Child extends React.Component { render () { return ( <div > <h3 > 子组件</h3 > </div > ) } } class Parent extends React.Component { render () { return ( <div > <h3 > 父组件</h3 > <Child /> </div > ) } } class App extends React.Component { render () { return ( <div > <h1 > 父子组件</h1 > <Parent /> </div > ) } } export default App
5.2.2 父组件给子组件传值 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './01_props/02_Parent_Child_value' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/01_props/02_Parent_Chil_value.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 import React from 'react' const Child2 = (props ) => { console .log ('props2' , props) return ( <div > <h3 > 子组件2</h3 > <div > str的值为{ props.str }</div > <div > flag的值为{ props.flag + ''}</div > <div > num的值为{ props.num }</div > <div > obj的a值为{ props.obj.a }</div > <div > arr的值为{ props.arr }</div > </div > ) } class Child1 extends React.Component { render () { console .log ("props1" , this .props ) return ( <div > <h3 > 子组件1</h3 > <div > str的值为{ this.props.str }</div > <div > flag的值为{ this.props.flag + ''}</div > <div > num的值为{ this.props.num }</div > <div > obj的a值为{ this.props.obj.a }</div > <div > arr的值为{ this.props.arr }</div > </div > ) } } class Parent extends React.Component { render () { const str = "hello world" return ( <div > <h3 > 父组件</h3 > <Child1 str = { str } flag = { true } num = { 100 } obj = { { a: 1 , b: 2 } } arr = { ['a ', 'b ', 'c '] } /> <Child2 str = { str } flag = { false } num = { 10000 } obj = { { a: 10 , b: 20 } } arr = { ['aa ', 'bb ', 'cc '] } /> </div > ) } } class App extends React.Component { render () { return ( <div > <h1 > 父子组件</h1 > <Parent /> </div > ) } } export default App
5.2.3 父组件给子组件传值设置默认值 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './01_props/03_Parent_Child_default' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/01_props/03_Parent_Chil_default.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 import React from 'react' const Child2 = (props ) => { console .log ('props2' , props) return ( <div > <h3 > 子组件2</h3 > <div > str的值为{ props.str }</div > <div > flag的值为{ props.flag + ''}</div > <div > num的值为{ props.num }</div > <div > obj的a值为{ props.obj.a }</div > <div > arr的值为{ props.arr }</div > </div > ) } Child2 .defaultProps = { str : 'hello react function' } class Child1 extends React.Component { static defaultProps = { str : 'hello react static props' } render () { console .log ("props1" , this .props ) return ( <div > <h3 > 子组件1</h3 > <div > str的值为{ this.props.str }</div > <div > flag的值为{ this.props.flag + ''}</div > <div > num的值为{ this.props.num }</div > <div > obj的a值为{ this.props.obj.a }</div > <div > arr的值为{ this.props.arr }</div > </div > ) } } class Parent extends React.Component { render () { const str = "hello world" return ( <div > <h3 > 父组件</h3 > <Child1 str = { str } flag = { true } num = { 100 } obj = { { a: 1 , b: 2 } } arr = { ['a ', 'b ', 'c '] } /> <Child2 flag = { false } num = { 10000 } obj = { { a: 10 , b: 20 } } arr = { ['aa ', 'bb ', 'cc '] } /> </div > ) } } class App extends React.Component { render () { return ( <div > <h1 > 父子组件</h1 > <Parent /> </div > ) } } export default App
5.2.4 使用prop-types属性验证 自 React v15.5 起,React.PropTypes 已移入另一个包中。请使用 prop-types 库
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 import PropTypes from 'prop-types' ;MyComponent .propTypes = {optionalArray : PropTypes .array ,optionalBool : PropTypes .bool ,optionalFunc : PropTypes .func ,optionalNumber : PropTypes .number ,optionalObject : PropTypes .object ,optionalString : PropTypes .string ,optionalSymbol : PropTypes .symbol ,optionalNode : PropTypes .node ,optionalElement : PropTypes .element ,optionalElementType : PropTypes .elementType ,optionalMessage : PropTypes .instanceOf (Message ),optionalEnum : PropTypes .oneOf (['News' , 'Photos' ]),optionalUnion : PropTypes .oneOfType ([ PropTypes .string , PropTypes .number , PropTypes .instanceOf (Message ) ]), optionalArrayOf : PropTypes .arrayOf (PropTypes .number ),optionalObjectOf : PropTypes .objectOf (PropTypes .number ),optionalObjectWithShape : PropTypes .shape ({ color : PropTypes .string , fontSize : PropTypes .number }), optionalObjectWithStrictShape : PropTypes .exact ({ name : PropTypes .string , quantity : PropTypes .number }), requiredFunc : PropTypes .func .isRequired ,requiredAny : PropTypes .any .isRequired ,customProp : function (props, propName, componentName ) { if (!/matchme/ .test (props[propName])) { return new Error ( 'Invalid prop `' + propName + '` supplied to' + ' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.' ); } }, customArrayProp : PropTypes .arrayOf (function (propValue, key, componentName, location, propFullName ) { if (!/matchme/ .test (propValue[key])) { return new Error ( 'Invalid prop `' + propFullName + '` supplied to' + ' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.' ); } }) };
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './01_props/04_Parent-Child_type' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/01_props/04_Parent_Chil_type.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 import React from 'react' import PropTypes from 'prop-types' const Child2 = (props ) => { console .log ('props2' , props) return ( <div > <h3 > 子组件2</h3 > <div > str的值为{ props.str }</div > <div > flag的值为{ props.flag + ''}</div > <div > num的值为{ props.num }</div > <div > obj的a值为{ props.obj.a }</div > <div > arr的值为{ props.arr }</div > </div > ) } Child2 .defaultProps = { str : 'hello react function' } Child2 .propTypes = { str : PropTypes .string .isRequired , flag : PropTypes .bool , obj : PropTypes .object , arr : PropTypes .array , num : function (props, propName, componentName ) { console .log (props) console .log (propName) console .log (componentName) if (typeof props[propName] !== 'number' ) { return new Error ('请传入number类型数据' ) } if (props[propName] < 1000 ) { return new Error ('出错了' ) } } } class Child1 extends React.Component { static defaultProps = { str : 'hello react static props' } render () { console .log ("props1" , this .props ) return ( <div > <h3 > 子组件1</h3 > <div > str的值为{ this.props.str }</div > <div > flag的值为{ this.props.flag + ''}</div > <div > num的值为{ this.props.num }</div > <div > obj的a值为{ this.props.obj.a }</div > <div > arr的值为{ this.props.arr }</div > </div > ) } } class Parent extends React.Component { render () { const str = "hello world" return ( <div > <h3 > 父组件</h3 > <Child1 str = { str } flag = { true } num = { 100 } obj = { { a: 1 , b: 2 } } arr = { ['a ', 'b ', 'c '] } /> <Child2 flag = { false } num = '100' obj = { { a: 10 , b: 20 } } arr = { ['aa ', 'bb ', 'cc '] } /> </div > ) } } class App extends React.Component { render () { return ( <div > <h1 > 父子组件</h1 > <Parent /> </div > ) } } export default App
5.3 props.children 我们知道使用组件的时候,可以嵌套。要在自定义组件中使用嵌套结构,就需要使用 props.children 。
等同于 vue中的 slot 插槽
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './01_props/05_App_props_children' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/01_props/05_App_props_children.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;const Content = (props ) => { return ( <div > { props.children }</div > ) } class Header extends Component { render () { return ( <header > { this.props.children }</header > ) } } class App extends Component { render ( return ( <div > <Header > 这里是首页头部</Header > <Content > 这里是首页内容</Content > <hr /> <Header > 这里是分类头部</Header > <Content > 这里是分类内容</Content > </div > ); } } export default App ;
如果需要给组件添加多个元素,并且显示在多个位置,可以如下设置:
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './01_props/06_App_mutiple_props_children' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/01_props/06_App_mutiple_props_children.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;const Header = (props ) => { console .log (props.children ) return ( <header > <ul > <li > { props.children[0] }</li > <li > { props.children[1] }</li > <li > { props.children[2] }</li > </ul > </header > ) } class App extends Component { render ( return ( <div > <Header > <div > 城市</div > <div > 标题</div > <div > 登录</div > </Header > <Header > <div > 返回</div > <div > 产品名称</div > <div > 更多</div > </Header > </div > ); } } export default App ;
实现类似vue的具名插槽,需要通过 props.children 的下标去访问
5.4 render props特性 使用 Render Props 来解决横切关注点(Cross-Cutting Concerns)
组件是 React 代码复用的主要单元,但如何将一个组件封装的状态或行为共享给其他需要相同状态的组件并不总是显而易见。
以下组件跟踪 Web 应用程序中的鼠标位置:
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './01_props/07_App_mouse_tracker' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/01_props/07_App_mouse_tracker.jsx
还没有学习状态state以及事件处理,这里先用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { x : 0 , y : 0 } render ( return ( <div style ={ { width: '100vw ', height: '100vh ' } } onMouseMove = { (event ) => { // 修改状态 -- 不要使用赋值表达式 this.setState({ x: event.clientX, y: event.clientY }) } }> <p > 鼠标位置:({ this.state.x }, { this.state.y })</p > </div > ); } } export default App ;
当光标在屏幕上移动时,组件在 <p> 中显示其坐标。
现在的问题是:我们如何在另一个组件中复用这个行为?换个说法,若另一个组件需要知道鼠标位置,我们能否封装这一行为,以便轻松地与其他组件共享它?
render prop 是一个用于告知组件需要渲染什么内容的函数 prop。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './01_props/08_App_render_props' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/01_props/08_App_render_props.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;const Cat = (props ) => { return ( <div > cat鼠标位置:({ props.point.x }, { props.point.y })</div > ) } const Dog = (props ) => { return ( <div > Dog鼠标位置:({ props.point.x }, { props.point.y })</div > ) } class Mouse extends Component { state = { x : 0 , y : 0 } render ( return ( <div style ={ { width: '100vw ', height: '50vh ' } } onMouseMove = { (event ) => { // 修改状态 -- 不要使用赋值表达式 this.setState({ x: event.clientX, y: event.clientY }) } }> <p > mouse鼠标位置:({ this.state.x }, { this.state.y })</p > { this.props.render(this.state) } </div > ); } } class App extends Component { render () { return ( <div > {/* <Mouse render = { (point ) => { return <Cat point = { point }> </Cat > } }></Mouse > <hr /> <Mouse render = { (point ) => { return <Dog point = { point }> </Dog > } }></Mouse > */} <Mouse render = { (point ) => { return ( <> <Cat point = { point }> </Cat > <Dog point = { point }> </Dog > </> ) }}></Mouse > </div> ) } } export default App ;
此案例实际上完成了react中子组件给父组件传值
六、State state 是 class组件的内置对象,用于class组件内部数据更新
state就是组件描述某种显示情况的数据,由组件自己设置和更改,也就是说由组件自己维护,使用state的目的就是为了在不同的状态下使组件的显示不同(自己管理)
6.1 state及其特点 State 与 props 类似,但是 state 是私有的,并且完全受控于当前组件
不要直接修改state
state更新可能是异步的:出于性能考虑,React 可能会把多个 setState() 调用合并成一个调用。
state更新会被合并:当你调用 setState() 的时候,React 会把你提供的对象合并到当前的 state
6.2 state的定义和使用 目前react中的状态有两种使用方式:
6.2.1 es6的类 - 构造函数 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './02_state/01_App_state_es6' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/02_state/01_App_state_es6.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { constructor (props) { super (props) this .state = { date : new Date () } } render ( return ( <div > 当前时间为:{ this.state.date.toLocaleDateString() + this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString() } </div > ); } } export default App ;
6.2.2 es7的类 - 属性初始化器 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './02_state/02_App_state_es7' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/02_state/02_App_state_es7.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { date : new Date () } render ( return ( <div > 当前时间为:{ this.state.date.toLocaleDateString() + this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString() }!! </div > ); } } export default App ;
6.3 如何正确的修改state setState() 将对组件 state 的更改排入队列,并通知 React 需要使用更新后的 state 重新渲染此组件及其子组件。这是用于更新用户界面以响应事件处理器和处理服务器数据的主要方式.
将 setState() 视为请求 而不是立即更新组件的命令。为了更好的感知性能,React 会延迟调用它,然后通过一次传递更新多个组件。
setState() 并不总是立即更新组件。它会批量推迟更新。这使得在调用 setState() 后立即读取 this.state 成为了隐患。为了消除隐患,请使用 componentDidUpdate 或者 setState 的回调函数(setState(updater, callback)),这两种方式都可以保证在应用更新后触发。
记住修改状态的三大原则:
1 2 state = { a : 10 } this .state .a = 100
1 2 3 4 5 state = { a : 10 } this .setState ({a : this .state .a + 1 })this .setState ({a : this .state .a + 1 })this .setState ({a : this .state .a + 1 })console .log (this .state .a )
6.4 this.setState()方法及其特点 setState() 会对一个组件的 state 对象安排一次更新。当 state 改变了,该组件就会重新渲染。
setState()可以添加两个参数,
setState() 的第二个参数为可选的回调函数,它将在 setState 完成合并并重新渲染组件后执行
6.4.1 传递函数 参数一为带有形式参数的 updater 函数:
1 this.setState((state, props) => stateChange[, callback] )
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './02_state/03_App_setState_function' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/02_state/03_App_setState_function.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { count : 100 } render ( return ( <div > { this.state.count } <button onClick ={ () => { this.setState((state, props) => { return { count: state.count + 1 } }, () => { console.log(4, this.state.count) // 103 }) console.log(1, this.state.count) // 100 this.setState((state, props) => { return { count: state.count + 1 } }, () => { console.log(5, this.state.count) // 103 }) console.log(2, this.state.count) // 100 this.setState((state, props) => { return { count: state.count + 1 } }, () => { console.log(6, this.state.count) // 103 }) console.log(3, this.state.count) // 100 } } >加1</button > </div > ); } } export default App ;
updater 函数中接收的 state 和 props 都保证为最新。updater 的返回值会与 state 进行浅合并。
6.4.2 传递对象 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './02_state/04_App_setState_object' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/02_state/04_App_setState_object.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { count : 100 } render ( return ( <div > { this.state.count } <button onClick ={ () => { this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 }, () => { console.log(4, this.state.count) // 101 }) console.log(1, this.state.count) // 100 this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 }, () => { console.log(5, this.state.count) // 101 }) console.log(2, this.state.count)// 100 this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 }, () => { console.log(6, this.state.count) // 101 }) console.log(3, this.state.count)// 100 } } >加1</button > </div > ); } } export default App ;
这种形式的 setState() 是异步的,并且在同一周期内会对多个 setState 进行批处理,相当于
1 2 3 4 5 6 Object.assign( prevState, {count: this.state.count + 1}, {count: this.state.count + 1}, ... )
后调用的 setState() 将覆盖同一周期内先调用 setState 的值,因此商品数仅增加一次。如果后续状态取决于当前状态,建议使用 updater 函数的形式代替(前面案例已经实现)。或者在第二个参数中再继续操作。
思考题:
1.何时以及为什么 setState() 会批量执行?
2.为什么不直接更新 this.state?
七、生命周期 组件的生命周期可分成三个状态:
Mounting(挂载,初始化):已插入真实 DOM Updating(更新,运行时):正在被重新渲染 Unmounting(卸载,销毁):已移出真实 DOM 生命周期图谱可以参考链接:https://projects.wojtekmaj.pl/react-lifecycle-methods-diagram/
类组件如何实现类似vue的计算属性: https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/blog/2018/06/07/you-probably-dont-need-derived-state.html#what-about-memoization
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './02_state/05_App_computed' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/02_state/05_App_computed.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;import memoize from 'memoize-one' class MemoList extends Component { state = { text : '' } filter = memoize ((list, text ) => { return list.filter (item =>'' && item.includes (text)) }) render () { const list = this .filter (this .props .list , this .state .text ) return ( <> <input type ="text" value ={ this.state.text } onChange = { (event ) => { this.setState({ text: event.target.value }) } }/> <ul > { list.map((item, index) => { return (<li key = { index }> { item } </li > ) }) } </ul > </> ) } } class App extends Component { state = { list : ['a' , 'ab' , 'abc' , 'abcd' ] } render ( return ( <div > <MemoList list ={this.state.list} /> </div > ); } } export default App ;
7.1 三个阶段 7.1.1 装载阶段 当组件实例被创建并插入 DOM 中时,其生命周期调用顺序如下:
constructor(): 在 React 组件挂载之前,会调用它的构造函数。
如果不需要对类组件添加初始化数据以及绑定事件,那么就不需要写 constructor
static getDerivedStateFromProps(): 在调用 render 方法之前调用,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用。
render(): render() 方法是 class 组件中唯一必须实现的方法。
componentDidMount(): 在组件挂载后(插入 DOM 树中)立即调用。
render() 方法是 class 组件中唯一必须实现的方法,其他方法可以根据自己的需要来实现。
7.1.2 更新阶段 每当组件的 state 或 props 发生变化时,组件就会更新。
当组件的 props 或 state 发生变化时会触发更新。组件更新的生命周期调用顺序如下:
static getDerivedStateFromProps(): 在调用 render 方法之前调用,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用。根据 shouldComponentUpdate() 的返回值,判断 React 组件的输出是否受当前 state 或 props 更改的影响。shouldComponentUpdate():当 props 或 state 发生变化时,shouldComponentUpdate() 会在渲染执行之前被调用。render(): render() 方法是 class 组件中唯一必须实现的方法。getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(): 在最近一次渲染输出(提交到 DOM 节点)之前调用。componentDidUpdate(): 在更新后会被立即调用,如果你需要执行副作用 (例如,数据提取或动画)以响应 props 中的更改。render() 方法是 class 组件中唯一必须实现的方法,其他方法可以根据自己的需要来实现。
7.1.3 卸载阶段 当组件从 DOM 中移除时会调用如下方法:
componentWillUnmount(): 在组件卸载及销毁之前直接调用。7.1.4 Error boundaries Error boundaries 是 React 组件,它会在其子组件树中的任何位置捕获 JavaScript 错误,并记录这些错误,展示降级 UI 而不是崩溃的组件树。Error boundaries 组件会捕获在渲染期间,在生命周期方法以及其整个树的构造函数中发生的错误。
项目中需要使用的最多的生命周期的钩子函数为 render, componentDidMount,componentDidUpdate,componentWillUnmount
详细介绍范例:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/392532496
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './02_state/06_App_lifeCycle' class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component { constructor (props ) { super (props); this .state = { hasError : false }; } static getDerivedStateFromError (error ) { return { hasError : true }; } componentDidCatch (error, info ) { console .log (info.componentStack ); } render ( if (this .state .hasError ) { return <h1 > Something went wrong.</h1 > } return this .props .children ; } } const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<ErrorBoundary > <App root = { root }/> </ErrorBoundary >
src/02_state/06_App_lifeCycle.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { count : 100 } componentDidMount () { this .setState ({ count : this .state .count + 100 }) } shouldComponentUpdate (nextProps, nextState) { return true } componentDidUpdate (prevProps, prevState, snapshot ) { } componentWillUnmount () { } render ( return ( <div > <p > { this.state.count }</p > <button onClick ={ () => { if (this.state.count === 210) { console.log('销毁组件') // 销毁组件 this.props.root.unmount() } else { this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 } ) } } }>加</button > </div > ); } } export default App ;
7.2 两个时期 将应用的渲染过程分为mount阶段(应用首次渲染)和update阶段(应用状态更新),无论在mount阶段还是update阶段,都会经历两个子阶段,一个是render阶段,一个是commit阶段。
mount时 :render阶段会根据jsx对象构建新的workInProgressFiber树,然后将相应的fiber节点标记为Placement,表示这个fiber节点需要被插入到dom树中,然后会这些带有副作用的fiber节点加入一条叫做Effect List的链表中。commit阶段会遍历render阶段形成的Effect List,执行链表上相应fiber节点的副作用,比如Placement插入,或者执行Passive(useEffect的副作用)。将这些副作用应用到真实节点上update时 :render阶段会根据最新状态的jsx对象对比current Fiber,再构建新的workInProgressFiber树,这个对比的过程就是diff算法,diff算法又分成单节点的对比和多节点的对比,对比的过程中同样会经历收集副作用的过程,也就是将对比出来的差异标记出来,加入Effect List中,这些对比出来的副作用例如:Placement(插入)、Update(更新)、Deletion(删除)等。commit阶段同样会遍历Effect List,将这些fiber节点上的副作用应用到真实节点上。
参考链接: https://blog.csdn.net/bemystery/article/details/121897223
7.3 入门理解React Fiber架构 在 React 16 之前,VirtualDOM 的更新采用的是Stack架构实现的,也就是循环递归方式。不过,这种对比方式有明显的缺陷,就是一旦任务开始进行就无法中断,如果遇到应用中组件数量比较庞大,那么VirtualDOM 的层级就会比较深,带来的结果就是主线程被长期占用,进而阻塞渲染、造成卡顿现象。
为了避免出现卡顿等问题,我们必须保障在执行更新操作时计算时不能超过16ms,如果超过16ms,就需要先暂停,让给浏览器进行渲染,后续再继续执行更新计算。而Fiber架构就是为了支持“可中断渲染”而创建的。
在React中,Fiber使用了一种新的数据结构fiber tree,它可以把虚拟dom tree转换成一个链表,然后再执行遍历操作,而链表在执行遍历操作时是支持断点重启的,示意图如下。
官方介绍中,Fiber 被理解为是一种数据结构,但是我们也可以将它理解为是一个执行单元。
Fiber 可以理解为一个执行单元,每次执行完一个执行单元,React Fiber就会检查还剩多少时间,如果没有时间则将控制权让出去,然后由浏览器执行渲染操作。React Fiber 与浏览器的交互流程如下图。
可以看到,React 首先向浏览器请求调度,浏览器在执行完一帧后如果还有空闲时间,会去判断是否存在待执行任务,不存在就直接将控制权交给浏览器;如果存在就会执行对应的任务,执行完一个新的任务单元之后会继续判断是否还有时间,有时间且有待执行任务则会继续执行下一个任务,否则将控制权交给浏览器执行渲染,这个流程是循环进行的。
所以,我们可以将Fiber 理解为一个执行单元,并且这个执行单元必须是一次完成的,不能出现暂停。并且,这个小的执行单元在执行完后计算之后,可以移交控制权给浏览器去响应用户,从而提升了渲染的效率。
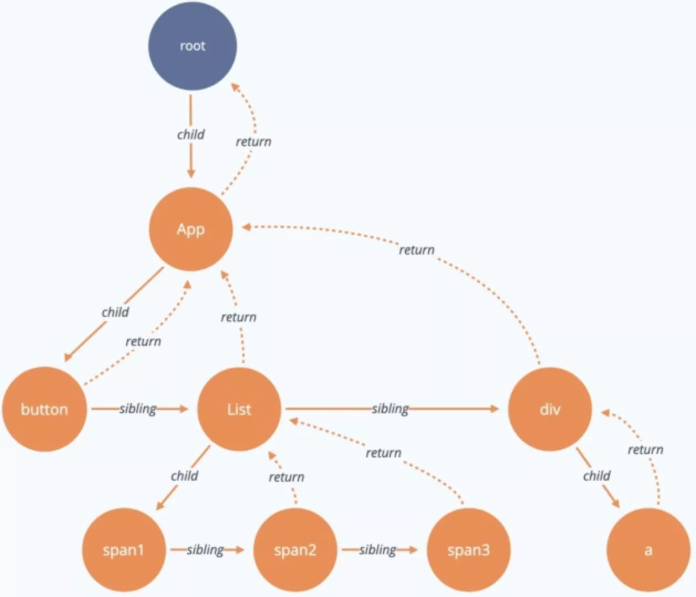
在官方的文档中,Fiber 被解释为是一种数据结构,即链表结构。在链表结构中,每个 Virtual DOM 都可以表示为一个 fiber,如下图所示。fiber包括了 child(第一个子节点)、sibling(兄弟节点)、return(父节点)等属性,React Fiber 机制的实现,就是依赖于上面的数据结构。
通过介绍,我们知道Fiber使用的是链表结构,准确的说是单链表树结构 。为了方便理解 Fiber 的遍历过程,下面我们就看下Fiber链表结构。
在上面的例子中,每一个单元都包含了payload(数据)和nextUpdate(指向下一个单元的指针)两个元素
参考链接:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000042271919
八、事件绑定 React 元素的事件处理和 DOM 元素的很相似,但是有一点语法上的不同:
8.1 ES5语法绑定事件 8.1.1 无参数的绑定 8.1.1.1 方法一 1 2 3 4 handleClick(e) { // e - 事件对象 e.preventDefault(); // doSomething ... }
1 this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
1 <button onClick={this.hanleClick} />
8.1.1.1 方法二 1 2 3 4 handleClick(e) { // e - 事件对象 e.preventDefault(); // doSomething ... }
1 <button onClick={this.hanleClick.bind(this)} />
8.1.2 有参数的绑定 1 2 3 4 handleClick(param1, param2, e) { e.preventDefault(); // do something ... }
注意此时无论多少个参数, e 一定放在最后
1 <button onClick={this.hanleClick.bind(this, 'x', 'xx')} />
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './03_event/01_App_event_es5' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/03_event/01_App_event_es5.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { constructor (props) { super (props) this .handlerClickFn = this .handlerClick .bind (this ) } handlerClick (event) { console .log (1 , this ) } handlerParamsClick (a , b, event) { console .log ('a' , a) console .log ('b' , b) } render ( return ( <div > <button onClick ={ this.handlerClickFn }> es5绑定事件-构造函数</button > <button onClick ={ this.handlerClick.bind (this ) }> es5绑定事件-jsx改变this指向</button > <button onClick ={ this.handlerParamsClick.bind (this , '1 ', '2 ') }> es5绑定事件-传递参数</button > </div > ); } } export default App ;
8.2 ES6语法绑定事件 8.2.1 无参数绑定 8.2.1.1 方法一 1 2 3 4 handleClick = (e) => { e.preventDefault(); // do something ... }
1 <button onClick={this.hanleClick} />
比起 es 5 中的无参数函数的绑定调用, es 6 不需要使用 bind 函数;
8.2.1.2 方法二 jsx中定义箭头函数
1 <button onClick={ () => {}} />
8.2.2 有参数绑定 8.2.2.1 方法一 1 2 3 4 handleClick = (param1, e) => { e.preventDefault(); // do something ... }
1 <button onClick={this.hanleClick.bind(this, 'x')} />
有参数时,在绑定时依然要使用 bind;
8.2.2.2 方法二 1 2 3 handleClick = (param1, e) => { // do something ... }
1 2 3 <button onClick={() => this.handleClick('c')} /> // 如果需要对 event 对象进行处理的话,需要写成下面的格式 <button onClick={(e) => this.handleClick('c', e)} />
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './03_event/02_App_event_es6' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/03_event/02_App_event_es6.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { handlerClickFn = (event ) => { console .log (1 , this ) } handlerParamsClick = (a, b, event ) => { console .log ('a' , a) console .log ('b' , b) } render ( return ( <div > <button onClick ={ this.handlerClickFn }> es6绑定事件-定义箭头函数</button > <button onClick ={ (event ) => { // event 默认参数 console.log(2, this) } }>es6绑定事件-jsx写箭头函数</button > <button onClick ={ this.handlerParamsClick.bind (this , '1 ', '2 ') }> es6绑定事件-传递参数</button > <button onClick ={ (event ) => { // event 默认参数 console.log(2, this) // this.fetchData({ count: this.state.count }) } }>es6绑定事件-jsx写箭头函数,直接使用参数</button > </div > ); } } export default App ;
8.3 合成事件的特点 8.3.1 事件机制 react自身实现了一套事件机制,包括事件的注册、事件的存储、事件的合成及执行等。react 的所有事件并没有绑定到具体的dom节点上而是绑定在了document 上,然后由统一的事件处理程序来派发执行。通过这种处理,减少了事件注册的次数,另外react还在事件合成过程中,对不同浏览器的事件进行了封装处理,抹平浏览器之间的事件差异。 8.3.2 对合成事件的理解 (1)对原生事件的封装
react会根据原生事件类型来使用不同的合成事件对象,比如: 聚焦合成事件对象SyntheticFoucsEvent(合成事件对象:SyntheticEvent是react合成事件的基类,定义了合成事件的基础公共属性和方法。合成事件对象就是在该基类上创建的,原生js的 事件对象为 PointerEvent)
(2)不同浏览器事件兼容的处理
在对事件进行合成时,react针对不同的浏览器,也进行了事件的兼容处理
8.3.3 事件机制的流程 1、事件注册 在组件挂载阶段,根据组件内声明的事件类型-onclick,onchange 等,给 document 上添加事件 -addEventListener,并指定统一的事件处理程序 dispatchEvent。
2、事件存储 完成事件注册后,将 react dom ,事件类型,事件处理函数fn放入数组存储,组件挂载完成后,经过遍历把事件处理函数存储到 listenerBank(一个对象)中,缓存起来,为了在触发事件的时候可以查找到对应的事件处理方法去执行。
开始事件的存储,在 react 里所有事件的触发都是通过 dispatchEvent方法统一进行派发的,而不是在注册的时候直接注册声明的回调,来看下如何存储的 。react 把所有的事件和事件类型以及react 组件进行关联,把这个关系保存在了一个 map里,也就是一个对象里(键值对),然后在事件触发的时候去根据当前的 组件id和 事件类型查找到对应的 事件fn
3、事件执行 1、进入统一的事件分发函数(dispatchEvent)ReactDOMComponent对象
根据当前事件类型生成指定的合成对象 封装原生事件和冒泡机制 在 listenerBank事件池中查找事件回调并合成到 event(合成事件结束) 4.处理合成事件内的回调事件(事件触发完成 end)
8.3.4 合成事件、原生事件之间的冒泡执行关系 结论:
原生事件阻止冒泡肯定会阻止合成事件的触发。
合成事件的阻止冒泡不会影响原生事件。
原因:
浏览器事件的执行需要经过三个阶段,捕获阶段-目标元素阶段-冒泡阶段。 节点上的原生事件的执行是在目标阶段,然而合成事件的执行是在冒泡阶段,所以原生事件会先合成事件执行,然后再往父节点冒泡,所以原生事件阻止冒泡会阻止合成事件的触发,而合成事件的阻止冒泡不会影响原生事件。
九、条件渲染 在 React 中,你可以创建不同的组件来封装各种你需要的行为。然后还可以根据应用的状态变化只渲染其中的一部分。
React 中的条件渲染和 JavaScript 中的一致,使用 JavaScript 操作符 if 或条件运算符来创建表示当前状态的元素,然后让 React 根据它们来更新 UI。
9.1 && 你可以通过用花括号包裹代码在 JSX 中嵌入任何表达式 ,也包括 JavaScript 的逻辑与 &&,它可以方便地条件渲染一个元素。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './04_condition/01_App_condition_yu' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/04_condition/01_App_condition_yu.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class MainBox extends Component { render () { return ( <div > { this.props.unReadMessage.length > 0 && <span > 还有{ this.props.unReadMessage.length }条未读消息</span > }</div > ) } } class App extends Component { state = { message : ['a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' ] } render ( return ( <div > { this.state.message.map((item, index) => { return ( <p key = { index }> { item } <button onClick ={ () => { const arr = this.state.message // 获取数据 arr.splice(index, 1) // 处理数据 this.setState({ // 修改状态 message: arr }) }}>已读</button > </p > ) }) } <MainBox unReadMessage = { this.state.message } > </MainBox > </div > ); } } export default App ;
9.2 三元运算符 条件渲染的另一种方法是使用 JavaScript 的条件运算符:
1 condition ? true : false。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './04_condition/02_App_condition_san' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/04_condition/02_App_condition_san.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { loginState : false } render ( return ( <div > { this.state.loginState + '' } <button onClick ={ () => { this.setState({ loginState: !this.state.loginState }) } }>切换</button > { this.state.loginState ? <button > 退出</button > : <button > 登录</button > } </div > ); } } export default App ;
9.3 动态className Vue中有很方便的动态绑定 class属性的方式,v-bind:class,那么react怎么实现这样的效果呢?
<button class="btn btn-success btn-sm"></button>
<button class="btn btn-danger btn-sm"></button>
<button class="btn btn-warning btn-sm"></button>
{ this.state.type === 'success' ? 'btn btn-success btn-sm' : 'btn btn-sm'}
通过classnames这个插件可以实现
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './04_condition/03_App_condition_classname' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/04_condition/03_App_condition_classname.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;import classnames from 'classnames' class App extends Component { state = { type : 'default' , size : 'sm' } render ( return ( <div > <button className ={ classnames ({ 'btn ': true , 'btn-sm ': this.state.size === 'sm' , 'btn-success ': this.state.type === 'default' }) }> default</button > <button className ={ classnames ({ 'btn ': true , 'btn-md ': this.state.size === 'md' , 'btn-success ': this.state.type === 'success' }) }> success md</button > </div > ); } } export default App ;
补充:
1 $ cnpm i styled-components -S
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './04_condition/04_App_condition_cssinjs' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/04_condition/04_App_condition_cssinjs.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;import styled from 'styled-components' const ODiv = styled.div ` font-size: 30px; color: #f66 ` const Button = styled.button ` padding: 10px 30px; ` class App extends Component { render ( return ( <div > <ODiv > 你好</ODiv > <Button > 按钮</Button > </div > ); } } export default App ;
可以解决类似于 vue中 scoped
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './04_condition/05_App_module_css' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/04_condition/05_App_module_css.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;import style from './style.module.css' class App extends Component { render ( return ( <div className ={ style.container }> <div className ={ style.header }> </div > <div className ={ style.box }> </div > <div className ={ style.footer }> </div > </div > ); } } export default App ;
src/04_condition/style.module.css
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 .container { width : 100% ; height : 600px ; display : flex; flex-direction : column; } .header { width : 100% ; height : 50px ; background-color : #f66 ; } .box { width : 100% ; flex : 1 ; } .footer { width : 100% ; height : 50px ; background-color : #ccc ; }
9.4 动态style src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './04_condition/06_App_style' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/04_condition/06_App_style.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { size : 12 , color : '#333' } render ( return ( <> <button onClick ={ () => { this.setState({ size: this.state.size + 2 }) }}>字号+2</button > <input type ="color" value ={this.state.color} onChange ={(event) => { this.setState({ color: event.target.value }) }} /> <div style = { { fontSize: this.state.size , color: this.state.color } }> 中国共产党第十九届中央委员会第七次全体会议9日上午在京召开。中央委员会总书记习近平代表中央政治局向全会作工作报告,并就十九届中央委员会向中国共产党第二十次全国代表大会的报告讨论稿向全会作了说明。王沪宁就《中国共产党章程(修正案)》讨论稿向全会作了说明。 </div > </> ); } } export default App ;
十、列表渲染 使用 map() 方法遍历数组
组件接收数组参数,每个列表元素分配一个 key,不然会出现警告 a key should be provided for list items ,意思就是需要包含 key:
Keys 可以在 DOM 中的某些元素被增加或删除的时候帮助 React 识别哪些元素发生了变化。因此你应当给数组中的每一个元素赋予一个确定的标识。
一个元素的 key 最好是这个元素在列表中拥有的一个独一无二的字符串。通常,我们使用来自数据的id作为元素的 key
当元素没有确定的 id 时,你可以使用他的序列号索引 index 作为 key
如果列表可以重新排序,我们不建议使用索引来进行排序,因为这会导致渲染变得很慢。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './05_list/01_App_map' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/05_list/01_App_map.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { proList : [] } componentDidMount () { fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/list' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => console .log (res.data ) this .setState ({ proList : res.data }) }) } render ( const arr = [] this .state .proList .forEach ((item, index ) => { arr.push (<p key ={ item.proid }> { index + 1 } --- { item.proname }</p > }) return ( <div > { arr } </div > ); } } export default App ;
接口 http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/city/sortCity
实现多层遍历
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './05_list/02_App_mutiple_map' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/05_list/02_App_mutiple_map.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { cityList : [] } componentDidMount () { fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/city/sortCity' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => console .log (JSON .parse (res.data )) this .setState ({ cityList : JSON .parse (res.data ) }) }) } render ( const { cityList } = this .state return ( <div > <ul > { cityList && cityList.map(item => { return ( <li key = { item.letter }> { item.letter } <ol > { item.data && item.data.map(itm => ( <li key = { itm.cityId }> { itm.name }</li > )) } </ol > </li > ) }) } </ul > </div > ); } } export default App ;
十一、表单绑定 在 React 里,HTML 表单元素的工作方式和其他的 DOM 元素有些不同,这是因为表单元素通常会保持一些内部的 state。例如这个纯 HTML 表单只接受一个名称:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <form > <label > 名字: <input type ="text" name ="name" /> </label > <input type ="submit" value ="提交" /> </form >
此表单具有默认的 HTML 表单行为,即在用户提交表单后浏览到新页面。如果你在 React 中执行相同的代码,它依然有效。但大多数情况下,使用 JavaScript 函数可以很方便的处理表单的提交, 同时还可以访问用户填写的表单数据。实现这种效果的标准方式是使用“受控组件”。
表单元素的value值受 state的控制
11.1 各种表单的绑定与取值 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './06_form/01_App_form' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/06_form/01_App_form.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { userName : '' , password : '' , sex : '女' , hobby : [], lesson : 1 , note : '' , flag : false } handlerChange = (event ) => { console .log (event.target .name ) this .setState ({ [event.target .name ]: event.target .value }) } handlerHobbyChange = (event ) => { const checked = event.target .checked const value = event.target .value const arr = this .state .hobby if (checked) { arr.push (value) } else { const index = arr.findIndex (item => arr.splice (index, 1 ) } console .log (arr) this .setState ({ hobby : arr }) } handlerFlagChange = (event ) => { this .setState ({ flag : event.target .checked }) } render ( return ( <div > <div > {/* <input type ="text" placeholder ='用户名' value ={ this.state.userName } onChange = { this.handlerUserNameChange }/> { this.state.userName } */} {/* <input type ="text" placeholder ='用户名' value ={ this.state.userName } onChange = { this.handlerChange.bind (this , 'userName ') }/> { this.state.userName } */} <input type ="text" placeholder ='用户名' name ="userName" value ={ this.state.userName } onChange = { this.handlerChange }/> { this.state.userName } </div > <div > {/* <input type ="password" placeholder ='密码' value ={ this.state.password } onChange = { this.handlerPasswordChange }/> { this.state.password } */} {/* <input type ="password" placeholder ='密码' value ={ this.state.password } onChange = { this.handlerChange.bind (this , 'password ') }/> { this.state.password } */} <input type ="password" placeholder ='密码' name ="password" value ={ this.state.password } onChange = { this.handlerChange }/> { this.state.password } </div > <div > <input type ="radio" value ="男" name ="sex" checked ={ this.state.sex === '男' } onChange = { this.handlerChange }/> 男 <input type ="radio" value ="女" name ="sex" checked ={ this.state.sex === '女' } onChange = { this.handlerChange }/> 女 --- { this.state.sex } </div > <div > <input type ="checkbox" name ="hobby" value ="🏀" onChange ={ this.handlerHobbyChange }/> 🏀 <input type ="checkbox" name ="hobby" value ="⚽" onChange ={ this.handlerHobbyChange }/> ⚽ <input type ="checkbox" name ="hobby" value ="🏐" onChange ={ this.handlerHobbyChange }/> 🏐 <input type ="checkbox" name ="hobby" value ="🏓" onChange ={ this.handlerHobbyChange }/> 🏓 --- { this.state.hobby && this.state.hobby.map(item => { return <span key = { item }> {item}</span > }) } </div > <div > <select name ="lesson" value ={this.state.lesson} onChange ={ this.handlerChange }> <option value ={1} > 1阶段</option > <option value ={2} > 2阶段</option > <option value ={3} > 3阶段</option > </select > --- { this.state.lesson } </div > <div > <textarea name ='note' value ={ this.state.note } onChange = { this.handlerChange }> </textarea > </div > <div > <input type ="checkbox" checked = { this.state.flag } onChange = { this.handlerFlagChange } /> ***** 用户协议 -- { this.state.flag + ''} </div > </div > ); } } export default App ;
11.2 受控表单以及受控组件 在 HTML 中,表单元素(如<input>、 <textarea> 和 <select>)之类的表单元素通常自己维护 state,并根据用户输入进行更新。而在 React 中,可变状态(mutable state)通常保存在组件的 state 属性中,并且只能通过使用 setState()
我们可以把两者结合起来,使 React 的 state 成为“唯一数据源”。渲染表单的 React 组件还控制着用户输入过程中表单发生的操作。被 React 以这种方式控制取值的表单输入元素就叫做“受控组件”。
input、textarea、select 受控组件: value的属性受了 state 的控制
使用了受控组件,一定要写 value 属性以及onChange事件 radio、’checkbox’ 受控组件: checked 的属性受了state的控制
如果需要设置默认值,那么需要通过 defaultValue 以及defaultChecked设置
案例如上
十二、状态提升 在 React 中,将多个组件中需要共享的 state 向上移动到它们的最近共同父组件中,便可实现共享 state。这就是所谓的“状态提升”。
12.1 父子组件通信 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './07_state_up/01_App-parent-child-value' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/07_state_up/01_App-parent-child-value.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class Child1 extends Component { state = { count : 1 } render () { return ( <> <h1 > child1组件</h1 > { this.state.count } <button onClick ={ () => { this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1} ) }}>加1</button > </> ) } } class Child2 extends Component { state = { count : 1 } render () { return ( <> <h1 > child2组件</h1 > { this.state.count } <button onClick ={ () => { this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1} ) }}>加1</button > </> ) } } class App extends Component { render ( return ( <div > <Child1 > </Child1 > <hr > </hr > <Child2 > </Child2 > </div > ); } } export default App ;
我们发现Child1和Child2都是两个独立的个体,并没有实现数据共享
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './07_state_up/02_App_state_up' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/07_state_up/02_App_state_up.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class Child1 extends Component { render () { return ( <> <h1 > child1组件</h1 > {/* { this.state.count } */} { this.props.count } {/* <button onClick ={ () => { this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1} ) }}>加1</button > */} <button onClick ={ this.props.onClick }> 加1</button > </> ) } } class Child2 extends Component { render () { return ( <> <h1 > child2组件</h1 > {/* { this.state.count } */} { this.props.count } {/* <button onClick ={ () => { this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1} ) }}>加1</button > */} <button onClick ={ this.props.onClick }> 加1</button > </> ) } } class App extends Component { state = { count : 1 } add = () => { this .setState ({count : this .state .count + 1 }) } render ( return ( <div > <Child1 count = { this.state.count } onClick = { this.add }> </Child1 > <hr > </hr > <Child2 count = { this.state.count } onClick = { this.add }> </Child2 > </div > ); } } export default App ;
12.2 状态提升解读 实现方式是 利用最近的共同的父级组件中,用props的方式传过去到两个子组件,props中传的是一个setState的方法,通过子组件触发props传过去的方法,进而调用父级组件的setState的方法,改变了父级组件的state,调用父级组件的add方法,进而同时改变了两个子级组件的数据。
这是 两个有关连的同级组件 的传值,因为react的单项数据流,所以不在两个组件中进行传值,而是提升到 最近的共同的父级组件中,改变父级的state,进而影响了两个子级组件的render。
注意如果两个组件是同级组件(这两个组件的父组件是同一个)才考虑状态提升共享数据
十三、组合vs继承 React 有十分强大的组合模式。我们推荐使用组合而非继承来实现组件间的代码重用。
13.1 理解组件化 组件化是React的核心思想 :
组件化思想的应用 :
React的组件相对于Vue更加的灵活和多样,按照不同的方式可以分成很多类 组件 :
根据组件的定义方式,可以分为:函数组件(Functional Component )和类组件(Class Component); vue 中有没有类组件和函数式组件?vue2中有
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <template> </template> <script> export default { props:[], data () { return {} } } </script>
vue中的函数式组件 - 无状态组件,所有的数据来源均来自父组件 1 2 3 4 <template functional> <div > {{props.msg}}</div > </template>
1 2 3 4 5 <template> <div>hello vue</div> </template> class Home extends Vue {} // export default {}
根据组件内部是否有状态需要维护,可以分成:无状态组件(Stateless Component )和有状态组件(Stateful Component);
根据组件的不同职责,可以分成:展示型组件(Presentational Component - 只做数据的展示,一般不需要写更多的业务逻辑-数据请求不出现在展示型组件-顶多发出请求的指令-具体的请求交给容器型组件)和容器型组件(Container Component - 负责给展示性组件提供数据以及处理展示型组件需要的具体的业务逻辑) - 状态管理器-更容易理解;
这些概念有很多重叠,但是他们最主要是关注数据逻辑和UI展示的分离:
函数组件、无状态组件、展示型组件主要关注UI的展示; 类组件、有状态组件、容器型组件主要关注数据逻辑; 13.2 使用组合而非继承实现React组件化 有些组件无法提前知晓它们子组件的具体内容,建议这些组件使用一个特殊的 children prop 来将他们的子组件传递到渲染结果中。
参照5.3章节
少数情况下,你可能需要在一个组件中预留出几个“洞”。这种情况下,我们可以不使用 children,而是自行约定:将所需内容传入 props,并使用相应的 prop。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './08_com/01_App_props_slot' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/08_com/01_App_props_slot.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class Header extends Component { render () { return ( <header > <ul > <li > { this.props.left }</li > <li > { this.props.default }</li > <li > { this.props.right }</li > </ul > { this.props.children } </header > ) } } class Header1 extends Component { render () { return ( <header > <ul > <li > { this.props.children[0] }</li > <li > { this.props.children[1] }</li > <li > { this.props.children[2] }</li > </ul > </header > ) } } class App extends Component { render ( return ( <div > <Header left = { <span > logo</span > } default = { <span > 搜索框</span > } right = { <span > 登录</span > } > 1111111111 </Header > <Header left = { <span > 返回</span > } default = { <span > 标题</span > } right = { <span > 更多</span > } ></Header > <hr /> <Header1 > <span > logo</span > <span > 搜索框</span > <span > 登录</span > </Header1 > <Header1 > <span > 返回</span > <span > 标题</span > <span > 更多</span > </Header1 > </div > ); } } export default App ;
像 App组件中的left 和default以及 right 的 属性对应的之类的React 元素本质就是对象(object),所以你可以把它们当作 props,像其他数据一样传递。这种方法可能使你想起vue中“插槽”(slot)的概念,但在 React 中没有“插槽”这一概念的限制,你可以将任何东西作为 props 进行传递。
13.3 封装Modal弹窗 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './08_com/02_App_modal' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/08_com/02_App_modal.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class Modal extends Component { render () { return ( <div style ={ { position: 'fixed ', top: 0 , left: 0 , bottom: 0 , right: 0 , backgroundColor: 'rgba (0 ,0 ,0 , 0.4 )', display: 'flex ', justifyContent: 'center ', alignItems: 'center ' } }> <div style ={ { width: '50 %', minHeight: '300px ', backgroundColor: '#fff ' } }> 这里是一个模态框 <button onClick ={ this.props.onClick }> 关闭</button > </div > </div > ) } } class App extends Component { state = { show : false } close = () => { this .setState ({ show : false }) } render ( return ( <div > <button onClick ={ () => this.setState({ show: true })}>打开模态框</button > { this.state.show ? <Modal onClick = { this.close }/> : null } </div > ); } } export default App ;
审查元素发现 Modal 组件是渲染在原来的组件的位置的,如果想要让它渲染到不同的位置怎么办呢?
13.4 ReactDOM.createPortal() 普通的组件,子组件的元素将挂载到父组件的DOM节点中。
有时需要将元素渲染到DOM中的不同位置上去,这是就用到的portal的方法。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './08_com/03_App_portal' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/08_com/03_App_portal.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;import ReactDOM from 'react-dom' class Modal extends Component { modalRef = React .createRef () render () { return ReactDOM .createPortal ( <div id ='modal' ref = { this.modalRef } style ={ { position: 'fixed ', top: 0 , left: 0 , bottom: 0 , right: 0 , backgroundColor: 'rgba (0 ,0 ,0 , 0.4 )', display: 'flex ', justifyContent: 'center ', alignItems: 'center ' } } // onClick = { this.props.onClick } onClick = { (event ) => { console.log(event.target) console.log(document.getElementById('modal')) console.log(this.modalRef) // if (event.target === document.getElementById('modal')) { // ? id ? // if (event.target === this.refs.modal) { // ? ref 删除线? if (event.target === this.modalRef.current) { // ref的使用 // 如何判断当前点击的是自身而不是子元素 this.props.onClick() } } } > <div style ={ { width: '50 %', minHeight: '300px ', backgroundColor: '#fff ' } } // onClick = { event => { // event.stopPropagation() // } } > 这里是一个模态框 <button onClick ={ this.props.onClick }> 关闭</button > </div > </div > , document .getElementsByTagName ('body' )[0 ] ) } } class App extends Component { state = { show : false } close = () => { this .setState ({ show : false }) } render ( return ( <div > <button onClick ={ () => this.setState({ show: true })}>打开模态框</button > { this.state.show ? <Modal onClick = { this.close }/> : null } </div > ); } } export default App ;
一个 portal 的典型用例是当父组件有 overflow: hidden 或 z-index 样式时,但你需要子组件能够在视觉上“跳出”其容器。例如,对话框、悬浮卡以及提示框:
十四、上下文Context 14.1 理解上下文、作用及其特点 Context 提供了一个无需为每层组件手动添加 props,就能在组件树间进行数据传递的方法。
Context 设计目的是为了共享那些对于一个组件树而言是“全局”的数据,例如当前认证的用户、主题或首选语言。
Context 主要应用场景在于很多 不同层级的组件需要访问同样一些的数据。请谨慎使用,因为这会使得组件的复用性变差。
14.2 使用React.createContext() 14.2.1 逐层传递数据 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './09_context/01_App_next_value' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/09_context/01_App_next_value.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class Third extends Component { render () { return ( <div > <h3 > third</h3 > <div > { this.props.val }</div > </div > ) } } const Second = (props ) => { return ( <div > <h2 > second</h2 > <Third val = { props.val }/> </div > ) } const First = (props ) => { return ( <div > <h1 > first</h1 > <Second val ={ props.val }/> </div > ) } class App extends Component { render ( return ( <div > <First val ="传家宝" /> </div > ); } } export default App ;
14.2.2 使用Context传值 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './09_context/02_App_context' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/09_context/02_App_context.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;const LangContext = React .createContext ()class Third extends Component { render () { return ( <div > <h3 > third</h3 > <LangContext.Consumer > { (val) => { return ( <div > 语言为: { val }</div > ) } } </LangContext.Consumer > </div > ) } } const Second = ( return ( <div > <h2 > Second</h2 > <Third /> </div > ) } const First = ( return ( <div > <h1 > First</h1 > <Second /> </div > ) } class App extends Component { state = { lang : 'zh' } render ( return ( <div > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'zh'})}>中文</button > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'en'})}>英文</button > {/* 2.祖先组件通过 上下文对象的Provider 组件 配合value进行传值 */} <LangContext.Provider value ={this.state.lang} > <First /> </LangContext.Provider > </div > ); } } export default App ;
14.2.3 传递多个值 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './09_context/03_App_context_multiple_value' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/09_context/03_App_context_multiple_value.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;const LangContext = React .createContext ()const ColorContext = React .createContext ()class Third extends Component { render () { return ( <div > <h3 > third</h3 > <ColorContext.Consumer > { (color) => { return ( <> <LangContext.Consumer > { (val) => { return ( <div style = {{ color: color }}> 语言为: { val }</div > ) } } </LangContext.Consumer > </> ) } } </ColorContext.Consumer > </div> ) } } const Second = ( return ( <div > <h2 > Second</h2 > <Third /> </div > ) } const First = ( return ( <div > <h1 > First</h1 > <Second /> </div > ) } class App extends Component { state = { lang : 'zh' , color : '#f66' } render ( return ( <div > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'zh'})}>中文</button > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'en'})}>英文</button > <input type ="color" value ={ this.state.color } onChange = { (event ) => { this.setState({ color: event.target.value }) }}/> {/* 2.祖先组件通过 上下文对象的Provider 组件 配合value进行传值 */} <LangContext.Provider value ={this.state.lang} > <ColorContext.Provider value = { this.state.color }> <First /> </ColorContext.Provider > </LangContext.Provider > </div > ); } } export default App ;
上述案例,还可以通过一个上下文对象传递多个值
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './09_context/04_App_one_context_multiple_value' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/09_context/04_App_one_context_multiple_value.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;const MyContext = React .createContext ()class Third extends Component { render () { return ( <div > <h3 > third</h3 > <MyContext.Consumer > { (val) => { return ( <div style = {{ color:val.color }}> 3语言为: { val.lang }</div > ) } } </MyContext.Consumer > </div > ) } } const Second = ( return ( <div > <h2 > Second</h2 > <Third /> </div > ) } const First = ( return ( <div > <h1 > First</h1 > <Second /> </div > ) } class App extends Component { state = { lang : 'zh' , color : '#f66' } render ( return ( <div > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'zh'})}>中文</button > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'en'})}>英文</button > <input type ="color" value ={ this.state.color } onChange = { (event ) => { this.setState({ color: event.target.value }) }}/> {/* 2.祖先组件通过 上下文对象的Provider 组件 配合value进行传值 */} <MyContext.Provider value ={ { lang: this.state.lang , color: this.state.color } }> <First /> </MyContext.Provider > </div > ); } } export default App ;
如果遇到函数式组件如何获取Context的值
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './09_context/05_App_function_context_value' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/09_context/05_App_function_context_value.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;import { useContext } from 'react' ;const LangContext = React .createContext ()class Third extends Component { render () { return ( <div > <h3 > third</h3 > <LangContext.Consumer > { (val) => { return ( <div > 语言为: { val }</div > ) } } </LangContext.Consumer > </div > ) } } const Second = ( return ( <div > <h2 > Second</h2 > <LangContext.Consumer > { (val) => { return ( <div > Second - 语言为: { val }</div > ) } } </LangContext.Consumer > <Third /> </div > ) } const First = ( const lang = useContext (LangContext ) return ( <div > <h1 > First</h1 > <div > First - 语言为: { lang }</div > <Second /> </div > ) } class App extends Component { state = { lang : 'zh' } render ( return ( <div > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'zh'})}>中文</button > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'en'})}>英文</button > {/* 2.祖先组件通过 上下文对象的Provider 组件 配合value进行传值 */} <LangContext.Provider value ={this.state.lang} > <First /> </LangContext.Provider > </div > ); } } export default App ;
如果浏览器安装过 react的开发者工具,打开之后发现上述代码,都显示为 Context.Provider 和 Context.Consumer,不好区分
加入 上下文对象的 displayName
14.2.4 displayName src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './09_context/06_App_context_displayName' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/09_context/06_App_context_displayName.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;const LangContext = React .createContext ()const ColorContext = React .createContext ()LangContext .displayName = 'LangContext' ColorContext .displayName = 'ColorContext' class Third extends Component { render () { return ( <div > <h3 > third</h3 > <ColorContext.Consumer > { (color) => { return ( <> <LangContext.Consumer > { (val) => { return ( <div style = {{ color: color }}> 语言为: { val }</div > ) } } </LangContext.Consumer > </> ) } } </ColorContext.Consumer > </div> ) } } const Second = ( return ( <div > <h2 > Second</h2 > <Third /> </div > ) } const First = ( return ( <div > <h1 > First</h1 > <Second /> </div > ) } class App extends Component { state = { lang : 'zh' , color : '#f66' } render ( return ( <div > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'zh'})}>中文</button > <button onClick ={() => this.setState({ lang: 'en'})}>英文</button > <input type ="color" value ={ this.state.color } onChange = { (event ) => { this.setState({ color: event.target.value }) }}/> {/* 2.祖先组件通过 上下文对象的Provider 组件 配合value进行传值 */} <LangContext.Provider value ={this.state.lang} > <ColorContext.Provider value = { this.state.color }> <First /> </ColorContext.Provider > </LangContext.Provider > </div > ); } } export default App ;
14.3 常见应用场景解读 共享那些对于一个组件树而言是“全局”的数据,例如当前认证的用户、主题或首选语言 配合react hooks 中的useReducer可以实现轻量的 redux 十五、高阶组件 高阶组件(HOC)是 React 中用于复用组件逻辑的一种高级技巧。
HOC 自身不是 React API 的一部分,它是一种基于 React 的组合特性而形成的设计模式。
具体而言,高阶组件是参数为组件,返回值为新组件的函数。
15.1 理解高阶组件、作用及其特点 一个高阶组件只是一个包装了另外一个 React 组件的 函数。
.实现了对原有组件的增强和优化。
可以对原有组件中的state, props和逻辑执行增删改操作, 一般用于代码重用和组件增强优化
15.2 高阶组件语法详解 我们想要我们的组件通过自动注入一个版权信息
15.2.1 组件嵌套 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './10_hoc/01_App-more-use' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/10_hoc/01_App-more-use.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class Footer extends Component { render () { return ( <footer > Copyright © 2022 Meta Platforms, Inc. </footer > ) } } class Page1 extends Component { state = { userName : '' } componentDidMount () { this .setState ({ userName : localStorage .getItem ('userName' ) }) } render () { return ( <div > <h1 > page1</h1 > <Footer /> </div > ) } } class Page2 extends Component { state = { userName : '' } componentDidMount () { this .setState ({ userName : localStorage .getItem ('userName' ) }) } render () { return ( <div > <h1 > page2</h1 > <Footer /> </div > ) } } class Page3 extends Component { state = { userName : '' } componentDidMount () { this .setState ({ userName : localStorage .getItem ('userName' ) }) } render () { return ( <div > <h1 > page3</h1 > <Footer /> </div > ) } } class App extends Component { render ( return ( <div > <Page1 /> <hr /> <Page2 /> <hr /> <Page3 /> </div > ); } } export default App ;
通过Footer组件可以复用jsx代码,但是其余的业务逻辑代码显得无能为力,可以通过高阶组件来实现
15.2.2 高阶组件 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './10_hoc/02_App-more-use-hoc' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render (<App />
src/10_hoc/02_App-more-use-hoc.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;localStorage .setItem ('userName' , '吴大勋' )class Footer extends Component { render () { return ( <footer > Copyright © 2022 Meta Platforms, Inc. </footer > ) } } const withFooter = (Com ) => { return class extends Component { state = { userName : '' } componentDidMount () { console .log ('0000' ) this .setState ({ userName : localStorage .getItem ('userName' ) }) } render () { return ( <> <Com userName = { this.state.userName }/> <Footer /> </> ) } } } class Page1 extends Component { componentDidMount () { console .log ('1111' ) } render () { return ( <div > {/* <h1 > page1 - { this.state.userName }</h1 > */} <h1 > page1 - { this.props.userName }</h1 > {/* <Footer /> */} </div > ) } } Page1 = withFooter (Page1 )class Page2 extends Component { render () { return ( <div > {/* <h1 > page2 - { this.state.userName }</h1 > */} <h1 > page2 - { this.props.userName }</h1 > {/* <Footer /> */} </div > ) } } Page2 = withFooter (Page2 )class Page3 extends Component { render () { return ( <div > {/* <h1 > page3 - { this.state.userName }</h1 > */} <h1 > page3 - { this.props.userName }</h1 > {/* <Footer /> */} </div > ) } } Page3 = withFooter (Page3 )class App extends Component { render ( return ( <div > <Page1 /> <hr /> <Page2 /> <hr /> <Page3 /> </div > ); } } export default App ;
先执行了 组件的生命周期,后执行了高阶组件的生命周期
但是以后再复用组件的业务时,可以选用函数式组件的自定义hooks
15.3 常见应用场景解读 1.需要代码重用时, react如果有多个组件都用到了同一段逻辑, 这时,就可以把共同的逻辑部分提取出来,利用高阶组件的形式将这段逻辑整合到每一个组件中, 从而减少代码的逻辑重复
2.需要组件增强优化时, 比如我们在项目中使用的组件有些不是自己写的, 而是从网上撸下来的,但是第三方写的组件可能比较复杂, 有时不能完全满足需求, 但第三方组件不易修改, 此时也可以用高阶组件,在不修改原始组件的前提下, 对组件添加满足实际开发需求的功能
3.可以对原有组件中的state, props和逻辑执行增删改操作, 一般用于代码重用和组件增强优化
4.也可以用来替换 mixins 混入
父组件和高阶组件有什么区别?
首先从逻辑的执行流程上来看,高阶组件确实和父组件比较相像 但是高阶组件强调的是逻辑的抽象。高阶组件是一个函数,函数关注的是逻辑; 父组件是一个组件,组件主要关注的是UI/DOM。如果逻辑是与DOM直接相关的,那么这部分逻辑适合放到父组件中实现;如果逻辑是与DOM不直接相关的,那么这部分逻辑适合使用高阶组件抽象,如数据校验、请求发送等。 十六、ref Refs 提供了一种方式,允许我们访问 DOM 节点或在 render 方法中创建的 React 元素。
16.1 ref访问DOM src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './11_ref/01_App_ref' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <React.StrictMode > <App /> </React.StrictMode > )
src/11_ref/01_App_ref.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class App extends Component { state = { count : 1 } componentDidMount () { console .log (this .state .count ) this .setState ((state ) => { return { count : state.count + 1 } }) console .log ('id' , document .getElementById ('btn1' )) console .log ('refs' , this .refs .btn2 ) } render ( return ( <div > {/* 如果开启严格模式并且使用函数形式修改状态,输出结果为3 */} { this.state.count } <button id ='btn1' > 按钮1-id</button > <button ref ='btn2' > 按钮2-refs - 废弃</button > </div > ); } } export default App ;
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './11_ref/02_App_ref' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/11_ref/02_App_ref.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class Com extends Component { state = { name : '类组件' } testFn = () => { console .log (this .state .name + '!!!!!!!' ) } render () { return ( <div > 类组件ref的使用</div > ) } } const FunCom = ( return ( <div > 函数式组件ref</div > ) } class App extends Component { btn3Ref = React .createRef () comRef = React .createRef () funRef = React .createRef () componentDidMount () { console .log ('id' , document .getElementById ('btn1' )) console .log ('refs' , this .refs .btn2 ) console .log ('domCreateRef' , this .btn3Ref .current ) console .log ('comCreateRef' , this .comRef .current ) console .log ('FuncomCreateRef' , this .funRef .current ) } render ( return ( <div > <button id ='btn1' > 按钮1-id</button > <button ref ='btn2' > 按钮2-refs - 废弃</button > <button ref ={ this.btn3Ref }> 按钮2 - createRef </button > {/* 父组件可以直接通过ref 获取 子组件的实例 */} <Com ref = { this.comRef }> </Com > {/* 函数式组件没有实例,获取不到子组件实例 */} <FunCom ref = { this.funRef }> </FunCom > </div > ); } } export default App ;
如果在上述案例中,在FunCom组件中上使用ref,发现报了警告信息
Function components cannot be given refs. Attempts to access this ref will fail. Did you mean to use React.forwardRef()?
其原因是,函数式组件使用ref,必须使用React.forwardRef()方法二次包装
16.2 详解ref转发 Ref 转发是一个可选特性,其允许某些组件接收 ref,并将其向下传递(换句话说,“转发”它)给子组件。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './11_ref/03_App_ref_forward' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/11_ref/03_App_ref_forward.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 import React , { Component } from 'react' ;class Com extends Component { state = { name : '类组件' } testFn = () => { console .log (this .state .name + '!!!!!!!' ) } render () { return ( <div > 类组件ref的使用</div > ) } } const FunCom = React .forwardRef ((props, ref ) => { return ( <div ref ={ref} > 函数式组件ref</div > ) }) const Form = React .forwardRef ((props, ref ) => { return ( <form ref ={ref} > <input type ="text" name ='userName' /> <input type ="text" name ='password' /> <input type ="submit" value ="提交" /> {/* <input type ="reset" value ="重置" /> */} </form > ) }) class App extends Component { btn3Ref = React .createRef () comRef = React .createRef () funRef = React .createRef () formRef = React .createRef () componentDidMount () { console .log ('id' , document .getElementById ('btn1' )) console .log ('refs' , this .refs .btn2 ) console .log ('domCreateRef' , this .btn3Ref .current ) console .log ('comCreateRef' , this .comRef .current ) console .log ('FuncomCreateRef' , this .funRef .current ) console .log (this .formRef .current .children ) this .setFieldValue ({ userName : '吴大勋' , password : '123456' }) } setFieldValue = (obj ) => { this .formRef .current .children [0 ].value = obj.userName this .formRef .current .children [1 ].value = obj.password } render ( return ( <div > <button id ='btn1' > 按钮1-id</button > <button ref ='btn2' > 按钮2-refs - 废弃</button > <button ref ={ this.btn3Ref }> 按钮2 - createRef </button > {/* 父组件可以直接通过ref 获取 子组件的实例 */} <Com ref = { this.comRef }> </Com > {/* 函数式组件没有实例,获取不到子组件实例 */} <FunCom ref = { this.funRef }> </FunCom > <Form ref ={this.formRef} > </Form > <button onClick ={ () => { console.log(this.formRef.current) this.formRef.current.reset() }}>重置表单</button > </div > ); } } export default App ;
16.3 使用ref注意事项 当 ref 属性用于 HTML 元素时,使用 React.createRef() 创建的 ref 接收底层 DOM 元素作为其 current 属性。
当 ref 属性用于自定义 class 组件时,ref 对象接收组件的挂载实例作为其 current 属性。
你不能在函数组件上使用 ref 属性 ,因为他们没有实例。如果非要使用,实际上是转发ref(父组件中获取到了子组件的某个DOM)
十七、hooks 17.1 为什么使用hooks React 没有提供将可复用性行为“附加”到组件的途径(例如,把组件连接到 store)。如果你使用过 React 一段时间,你也许会熟悉一些解决此类问题的方案,比如 render props 和 高阶组件 。
Hook 使你在非 class 的情况下可以使用更多的 React 特性。 从概念上讲,React 组件一直更像是函数。而 Hook 则拥抱了函数,同时也没有牺牲 React 的精神原则。Hook 提供了问题的解决方案,无需学习复杂的函数式或响应式编程技术。
react 18版本以前hooks
17.2常见的hooks 17.2.1 useState src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/01_App_hooks_useState' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/01_App_hooks_useState.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 import React from 'react' ;import { useState } from 'react' ;const App = ( const [count, setCount] = useState (1 ) const [name, setName] = useState ('吴' ) function add100 () { setCount (count + 100 ) } const add1000 = ( setCount (count + 1000 ) } const add10000 = ( setCount (prevCount => console .log (prevCount) return prevCount + 10000 }) } return ( <div > { count } <button onClick ={ () => { // 修改函数内部的值为 运算之后的结果 setCount(count + 1) } }>加1</button > <button onClick ={ function () { // 修改函数内部的值为 运算之后的结果 setCount (count + 10 ) } }> 加10</button > <button onClick ={ add100 }> 加100</button > <button onClick ={ add1000 }> 加1000</button > <button onClick ={ add10000 }> 加10000</button > { name } <button onClick ={ () => { setName('吴大勋') } }>修改name</button > </div > ); }; export default App ;
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/02_App_hooks_useState_obj' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/02_App_hooks_useState_obj.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import React from 'react' ;import { useState } from 'react' ;const App = ( const [obj, setObj] = useState ({ w : 100 , h : 100 , x : 0 , y : 0 }) const mouseMove = (event ) => { setObj (prevObj => return Object .assign ({}, prevObj, { x : event.clientX }, { y : event.clientY }) }) } return ( <div style ={ { width: '100vw ', height: '100vh ' } } onMouseMove = { mouseMove }> <div > 元素的宽为: { obj.w },元素的高为: { obj.h }</div > <div > 元素的坐标点为: ({ obj.x },{ obj.y})</div > </div > ); }; export default App ;
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/03_App_hooks_useState_state' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/03_App_hooks_useState_state.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import React from 'react' ;import { useState } from 'react' ;const App = ( const [ box ] = useState ({ w : 100 , h : 100 }) const [position, setPosition] = useState ({ x : 0 , y : 0 }) const mouseMove = (event ) => { setPosition ({ x : event.clientX , y : event.clientY }) } return ( <div style ={ { width: '100vw ', height: '100vh ' } } onMouseMove = { mouseMove }> <div > 元素的宽为: { box.w },元素的高为: { box.h }</div > <div > 元素的坐标点为: ({ position.x },{ position.y})</div > </div > ); }; export default App ;
不要在循环,条件或嵌套函数中调用 Hook, 确保总是在你的 React 函数的最顶层以及任何 return 之前调用他们。
只在 React 函数中调用 Hook, 不要在普通的 JavaScript 函数中调用 Hook。你可以:
在 React 的函数组件中调用 Hook 在自定义 Hook 中调用其他 Hook 如果遇到需要以对象的形式定义状态时,根据需求划分对象,因为修改状态使用的是替换
17.2.2 useEffect src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/04_App_hooks_useEffect' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App root ={root}/ > )
src/12_hooks/04_App_hooks_useEffect.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import React , { useState, useEffect } from 'react' ;const App = (props ) => { const [proList, setProList] = useState ([]) const [count, setCount] = useState (1 ) useEffect (() => { fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/list' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => console .log (res.data ) setProList (res.data ) }) }, [count]) useEffect (() => { return () => { console .log ('组件销毁了' ) } }, [count]) return ( <div > <button onClick ={ () => { setCount(count + 1) if (count === 5) { props.root.unmount() } }}>加1</button > { count } <ul > { proList && proList.map(item => ( <li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname } </li > )) } </ul > </div > ); }; export default App ;
useEffect() 是个副作用函数。 useEffect() 函数在每次组件重新渲染时,可再次被调用。 在开发环境中,开启了 React.StrictMode 模式,组件开始时被渲染两次。 useEffect() 通过返回函数来清理副作用。 useEffect() 通过传递第二个参数数组来提高渲染性能,或者说实现 watch 效果。 17.2.3 useRef 利用 useRef 就可以绕过 Capture Value 的特性。可以认为 ref 在所有 Render 过程中保持着唯一引用,因此所有对 ref 的赋值或取值,拿到的都只有一个最终状态 ,而不会在每个 Render 间存在隔离。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/05_App_hooks_useRef' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/05_App_hooks_useRef.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 import React from 'react' ;import { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { useRef } from 'react' ;const FunCom = React .forwardRef ((props, ref ) => { return ( <div ref = { ref }> 函数式组件</div > ) }) class Com extends React.Component { state = { name : '类组件' } testFn = () => { console .log (this .state .name + '!!' ) } render () { return ( <div > 类组件</div > ) } } const App = ( const btnRef = useRef () const comRef = useRef () const funRef = useRef () useEffect (() => { console .log (btnRef.current ) console .log (comRef.current ) console .log (funRef.current ) }, []) return ( <div > <button ref = { btnRef }> 按钮ref</button > <Com ref = { comRef }/> <FunCom ref = { funRef }/> </div > ); }; export default App ;
17.2.4 useReducer useReducer 践行了 Flux/Redux 思想。使用步骤:
1、创建初始值initialState
2、创建所有操作 reducer(state, action);
3、传给 userReducer,得到读和写API
4、调用写 ({type: ‘操作类型’})
总的来说,useReducer 是 useState 的复杂版。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/06_App_hooks_useReducer' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/06_App_hooks_useReducer.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 import React , { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { useReducer } from 'react' ;const initialState = { bannerList : [], proList : [] } const reducer = (state, action ) => { switch (action.type ) { case 'CHANGE_BANNER_LIST' : return Object .assign ({}, state, { bannerList : action.payload }) case 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' : return { ...state, proList : action.payload } default : return state } } const App = ( const [state, dispatch] = useReducer (reducer, initialState) useEffect (() => { fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/banner/list' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_BANNER_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/list' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) }, []) return ( <div > { state.bannerList && state.bannerList.map(item => ( <img key = { item.bannerid } alt ={ item.alt } src = { item.img } style ={{ height: 100 }}/> )) } <ul > { state.proList && state.proList.map(item => ( <li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname } </li > )) } </ul > </div > ); }; export default App ;
如果遇到多个组件需要共享状态时,单纯useReducer就显得无能为力
17.2.5 useContext 1、使用 C = createContext(initial) 创建上下文
2、使用 <C.Provider> 圈定作用域
3、在作用域内使用 useContext(C)来使用上下文
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/07_App_hooks_useContext' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/07_App_hooks_useContext.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import React from 'react' ;import { useContext } from 'react' ;const LangContext = React .createContext ()const ColorContext = React .createContext ()const Second = ( const lang = useContext (LangContext ) const color = useContext (ColorContext ) return ( <> <h1 > Second</h1 > { lang } - { color } </> ) } const First = ( return ( <> <h1 > first</h1 > <Second /> </> ) } const App = ( return ( <div > <LangContext.Provider value = "中文" > <ColorContext.Provider value = "red" > <First /> </ColorContext.Provider > </LangContext.Provider > </div > ); }; export default App ;
使用 useReducer 和 useContext 实现轻型Redux,可以让组件间共享状态
步骤:
1、将数据集中在一个 store 对象
2、将所有操作集中在 reducer
3、创建一个 Context
4、创建对数据的读取 API
5、将第四步的内容放到第三步的 Context
6、用 Context.Provider 将 Context 提供给所有组件
7、各个组件用 useContext 获取读写API
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/08_App_hooks_redux' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/09-App-redux.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 import React from 'react' ;import { useContext } from 'react' ;import { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { useReducer } from 'react' ;const MyContext = React .createContext ()const intitalState = { userName : '吴大勋' , count : 100 , proList : [] } const reducer = (state, action ) => { switch (action.type ) { case 'CHANGE_USER_NAME' : return { ...state, userName : action.payload } case 'CHANGE_COUNT' : return { ...state, count : action.payload } case 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' : return { ...state, proList : action.payload } default : return state } } const Home = ( const { state, dispatch } = useContext (MyContext ) useEffect (() => { const fetchData = async ( const res = await fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/list' ).then (res =>json ()) dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' , payload : res.data }) } fetchData () }, [dispatch]) return ( <> <h1 > Home</h1 > <ul > { state.proList && state.proList.map(item => ( <li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname } </li > )) } </ul > </> ) } const List = ( const { state } = useContext (MyContext ) return ( <> <h1 > List</h1 > <ul > { state.proList && state.proList.map(item => ( <li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname } </li > )) } </ul > </> ) } const App = ( const [state, dispatch] = useReducer (reducer, intitalState) return ( <div > <MyContext.Provider value = { { state , dispatch }} > <Home /> <List /> </MyContext.Provider > </div > ); }; export default App ;
useContext + useReducer 可以实现轻型redux,但是不适合应用于多模块管理的大型项目
17.2.6 useMemo 17.2.7 useCallback src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/09_App_hooks_useCallback_useMemo' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/09_App_hooks_useCallback_useMemo.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 import React from 'react' ;import { useMemo } from 'react' ;import { useCallback } from 'react' ;import { useState } from 'react' ;const Child = React .memo ((props ) => { console .log ('child被执行了' ) return ( <div > child - { props.b }</div > ) }) const Com = React .memo ((props ) => { console .log ('com被执行了' ) return ( <div > com - { props.b }</div > ) }) const App = ( const [a, setA] = useState (0 ) const [b, setB] = useState (100 ) const [list, setList] = useState ([1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]) const add = ( setA (a + 1 ) } const addB = ( setB (b + 1 ) } const testFn = useMemo ((event ) => { }, []) const doubleA = useMemo (() => { return a * 2 }, [a]) const len = useMemo (() => { return list.length }, [list]) return ( <div > <button onClick ={ () => { const arr = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(list)) // 深拷贝 arr.push(len+1) setList(arr) }}>追加数据</button > {list} <button onClick ={ add }> a加1</button > { a } - { doubleA } - { len } <button onClick ={ addB }> b加1</button > { b } {/* 理想情况 b的值发生改变,Child 组件才被重新渲染 */} {/* 可以使用高阶组件 React.memo() 包裹一下Child组件 */} <Child b ={ b }/> {/* 组件的状态发生改变,组件重新渲染,重新渲染,就会给函数生成一个新的地址,意味着全新的一个属性 */} <Com b = { b } testFn = { testFn }/> </div > ); }; export default App ;
useCallback 应用于 组件的事件,使用useCallback 包裹组件 - 记忆函数
useMemo 可以是计算属性, 也应用于 组件的事件,使用useMemo 包裹组件 - 记忆组件
17.2.8 useImperativeHandle src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/10_App_hooks_useImperativeHandle.jsx' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/10_App_hooks_useImperativeHandle.jsx.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 import React from 'react' ;const Child = React .forwardRef ((props, ref ) => { const inputRef = React .useRef () const divRef = React .useRef () React .useImperativeHandle (ref, () => { return { inputFocus : () => { inputRef.current .focus () }, wirteVal (str) { divRef.current .innerHTML = str } } }) return ( <> <input ref = { inputRef }/> <div ref = { divRef }> </div > </> ) }) const App = ( const childRef = React .useRef () return ( <div > <button onClick ={ () => { // childRef.current.focus() childRef.current.inputFocus() }} style={{ marginRight: 30 }}>获取焦点</button > <button onClick ={ () => { // childRef.current.focus() childRef.current.wirteVal('hello hooks!!') }} style={{ marginRight: 30 }}>写入内容</button > <Child ref = { childRef }/> </div > ); }; export default App ;
上面这个例子中与直接转发 ref 不同,直接转发 ref 是将 React.forwardRef 中函数上的 ref 参数直接应用在了返回元素的 ref 属性上,其实父、子组件引用的是同一个 ref 的 current 对象,官方不建议使用这样的 ref 透传,而使用 useImperativeHandle 后,可以让父、子组件分别有自己的 ref,通过 React.forwardRef 将父组件的 ref 透传过来,通过 useImperativeHandle 方法来自定义开放给父组件的 current。
useImperativeHandle 的第一个参数是定义 current 对象的 ref,第二个参数是一个函数,返回值是一个对象,即这个 ref 的 current 对象,这样可以像上面的案例一样,通过自定义父组件的 ref 来使用子组件 ref 的某些方法。
useImperativeHandle 和React.forwardRef必须是配合使用的,这也是为什么在开头要介绍 ref 的转发。
17.2.9 useLayoutEffect useLayoutEffect 与 useEffect的区别:
useEffect 是异步执行的,而useLayoutEffect是同步执行的。useEffect 的执行时机是浏览器完成渲染之后,而 useLayoutEffect 的执行时机是浏览器把内容真正渲染到界面之前举个例子:
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/11_App_hooks_useLayoutEffect' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/13-App-useLayoutEffect.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import React , { useEffect, useLayoutEffect, useState } from 'react' ;function App ( const [ state1, setState1 ] = useState ('hello' ) const [ state2, setState2 ] = useState ('hi' ) useEffect (() => { let i = 0 while (i < 1000000000 ) { i++ } setState1 ('world' ) }, []) useLayoutEffect (() => { let i = 0 while (i < 1000000000 ) { i++ } setState2 ('world' ) }, []) return ( <> <h1 > {state1}</h1 > <h1 > {state2}</h1 > </> ) } export default App ;
注意观察 useEffect 抖动现象
useLayoutEffect 做DOM操作
useEffect 中 副作用执行
17.2.10 useDebugValue useDebugValue 可用于在 React 开发者工具中显示自定义 hook 的标签。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/12_App_hooks_useDebugValue' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/12_App_hooks_useDebugValue.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 import React , { useEffect, useState, useDebugValue } from 'react' ;const useCount = ( const [count, setCount] = useState (1 ) const add = ( setCount (count + 1 ) } useDebugValue ('myCount' ) return { count, add } } const useTitle = (count ) => { useEffect (() => { document .title = `点击了${count} 次` }) useDebugValue ('myTitle' ) } const App = ( const { count, add } = useCount () useTitle (count) return ( <div > <button onClick ={ add }> 加1</button > </div > ); }; export default App ;
接下来的hooks是属于react18版本新增的hooks
17.2.11 useId useId是一个钩子,用于生成唯一的ID,在服务器和客户端之间是稳定的,同时避免hydration 不匹配。
注意:
useId不是用来生成列表中的键的。Keys 应该从你的数据中生成。
不能用于列表渲染的key值
对于一个基本的例子,直接将id传递给需要它的元素。
对于同一组件中的多个ID,使用相同的ID附加一个后缀。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/13_App_hooks_useId' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/13_App_hooks_useId.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import React , { useId } from 'react' ;const App = ( const useNameId = useId () const passwordId = useId () return ( <div > { // list && list.map((item) => { // const id = useId() // 这样的写法是错误的 // return ( // <p key = { id }> { item } </p > // ) // }) } {/* HTML 中使用for,react中使用HtmlFor */} <div > <label htmlFor ={ useNameId }> 用户名</label > <input type ="text" id = { useNameId } /> </div > <div > <label htmlFor = { passwordId }> 密码</label > <input type ="password" id = { passwordId } /> </div > </div > ); }; export default App ;
注意:
useId 会生成一个包含 : token的字符串。这有助于确保令牌是唯一的,但在CSS选择器或API(如querySelectorAll)中不支持。
useId支持一个identifierPrefix,以防止在多根应用程序中发生碰撞。要配置,请参阅 hydrateRoot 和 ReactDOMServer 的选项。
hooks需要在函数式组件以及自定义hook的顶级使用(返回jsx代码之前),不要在jsx代码中使用hooks
17.2.12 useDeferredValue 真实需求其实不需要实时渲染所有的数据
useDeferredValue 需要接收一个值, 返回这个值的副本, 副本的更新会在值更新渲染之后进行更新, 以此来避免一些不必要的重复渲染. 打个比方页面中有输入框, 输入框下的内容依赖于输入框的值, 但是输入框是一个高频操作, 如果输入10次, 可能用户只想看到最终的结果那么中途的实时渲染就显得不那么重要了, 页面元素少点还好, 一旦元素过多页面就会及其的卡顿, 渲染引擎堵得死死的, 用户就会骂娘了, 此时使用useDeferredValue是一个很好的选择
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/14_App_hooks_useDeferredValue' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/14_App_hooks_useDeferredValue.jsx 数据量必须过大,否则看不到效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 import React , { useDeferredValue, useEffect, useState, useMemo, memo } from 'react' const List = memo (function List ({count} ) { const [data, setData] = useState ([]) useEffect (() => { const data = [] data.length = 50000 for (let i = 0 ; i < data.length ; i++) { data.fill (i+1 , i) } setData (data) }, [count]) return ( <div > { data.map((item) => { return ( <p key ={item} > {count}</p > ) }) } </div > ) }) export default function UseDeferredValueDemo ( const [inpVal, setInpVal] = useState ('' ) const deferredValue = useDeferredValue (inpVal) const memoList = useMemo (() => <List count ={deferredValue} > </List > return ( <> <h1 > UseDeferredValue</h1 > <input type ="text" value ={inpVal} onChange ={(e) => setInpVal(e.target.value)}/> {memoList} </> ) }
17.2.13 useTransition useTransition 又叫过渡, 他的作用就是标记非紧急更新, 这些被标记非紧急更新会在紧急更新完之后进行更新, useTransition 使用场景在应对渲染量很大的页面,需要及时响应某些事件的情况。
举个例子,准备一个进度条, 通过滑动进度条来显示进度条的进度并且渲染相同进度数量的div, 如果我们不对渲染进行优化那无疑页面会很卡, 此时使用过渡配合useMemo来缓存页面结构, diffing算法就会对比出少量的变化进行局部修改。
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from './12_hooks/15_App_hooks_useTransition' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> )
src/12_hooks/15_App_hooks_useTransition
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 import React , { useTransition, useState, useMemo } from 'react' export default function UseTransition ( const [isPending, startTransition] = useTransition () const [rangeValue, setRangeValue] = useState (1 ) const [renderData, setRenderData] = useState ([1 ]) const [isStartTransition, setIsStartTransition] = useState (false ) const handleChange = (e ) => { setRangeValue (e.target .value ) const arr = [] arr.length = e.target .value for (let i = 0 ; i <= arr.length ; i++) { arr.fill (i, i + 1 ) } if (isStartTransition) { startTransition (() => { setRenderData (arr) }) } else { setRenderData (arr) } } const jsx = useMemo (() => { return renderData.map ((item, index ) => { return ( <div style ={{ width: 50 , height: 50 , backgroundColor: `#${Math.floor (Math.random () * 16777215 ).toString ( 16 )}`, margin: 10 , display: 'inline-block ', }} key ={ 'item '+index } > {item} </div > ) }) }, [renderData]) return ( <div > <div style ={{ textAlign: 'center ' }}> <label > <input type ="checkbox" checked ={isStartTransition} onChange ={(e) => { setIsStartTransition(e.target.checked) }} /> useTransition </label > <input type ="range" value ={rangeValue} min ={0} max ={10000} style ={{ width: 120 }} onChange ={handleChange} /> <span > 进度条 {rangeValue}</span > <hr /> </div > {jsx} </div > ) }
17.2.14 useSyncExternalStore React18的beta版本将useMutableSource更新为了useSyncExternalStore,这个新的api将会对React的各种状态管理库产生非常大的影响,下面我来介绍useSyncExternalStore的用法和场景。
我们可以通过这个api自行设计一个redux + react-redux的数据方案:
1、设计store
首先我们要设计一个store,它必须有如下属性:
currentState:当前状态 subscribe:提供状态发生变化时的订阅能力 getSnapshot: 获取当前状态 以及改变state的方法,这里参考redux,设计了dispatch、reducer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 const store = { currentState :{data :0 }, listeners :[], reducer (action ){ switch (action.type ) { case 'ADD' : return {data :store.currentState .data +1 } default : return store.state } }, subscribe (l ){ store.listeners .push (l) }, getSnapshot ( return store.currentState }, dispatch (action ) { store.currentState = store.reducer (action) store.listeners .forEach (l =>l ()) return action; } }
2、应用 store 同步组件状态
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import React , { useSyncExternalStore } from 'react' import store from './store' export default function UseSyncExternalStoreDemo ( const state = useSyncExternalStore (store.subscribe , () => store.getSnapshot ().data ); return ( <div > <div > count: {state}</div > <div > <button onClick ={() => store.dispatch({type:'ADD'})}>add+</button > </div > </div > ) }
17.2.15 useInsertionEffect useInsertionEffect 与useEffect相同,在所有DOM变更之前同步触发。在使用 useLayoutEffect 读取布局之前,使用这个函数将样式注入到DOM中。因为这个钩子的作用域是有限的,所以这个钩子不能访问 refs,也不能调度更新。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 import React , { useInsertionEffect, useEffect, useLayoutEffect } from 'react' export default function UseInsertionEffect ( useInsertionEffect (() => { console .log ('useInsertionEffect' ) }) useEffect (() => { console .log ('useEffect' ) }) useLayoutEffect (() => { console .log ('useLayoutEffect' ) }) return ( <div className ="box" > UseInsertionEffect</div > ) }
17.3 自定义hooks 以use开头的小驼峰式的函数
十八、Redux 18.1 理解Flux架构 在2013年,Facebook让React亮相的同时推出了Flux框架,React的初衷实际上是用来替代jQuery的,Flux实际上就可以用来替代Backbone.js,Ember.js等一系列MVC架构的前端JS框架。
其实Flux在React里的应用就类似于Vue中的Vuex的作用,但是在Vue中,Vue是完整的mvvm框架,而Vuex只是一个全局的插件。
React只是一个MVC中的V(视图层),只管页面中的渲染,一旦有数据管理的时候,React本身的能力就不足以支撑复杂组件结构的项目,在传统的MVC中,就需要用到Model和Controller。Facebook对于当时世面上的MVC框架并不满意,于是就有了Flux, 但Flux并不是一个MVC框架,他是一种新的思想。
View: 视图层 ActionCreator(动作创造者):视图层发出的消息(比如mouseClick) Dispatcher(派发器):用来接收Actions、执行回调函数 Store(数据层):用来存放应用的状态,一旦发生变动,就提醒Views要更新页面 Flux的流程:
组件获取到store中保存的数据挂载在自己的状态上 用户产生了操作,调用actions的方法 actions接收到了用户的操作,进行一系列的逻辑代码、异步操作 然后actions会创建出对应的action,action带有标识性的属性 actions调用dispatcher的dispatch方法将action传递给dispatcher dispatcher接收到action并根据标识信息判断之后,调用store的更改数据的方法 store的方法被调用后,更改状态,并触发自己的某一个事件 store更改状态后事件被触发,该事件的处理程序会通知view去获取最新的数据 18.2 理解Redux单向数据流流程 React 只是 DOM 的一个抽象层,并不是 Web 应用的完整解决方案。有两个方面,它没涉及。
2013年 Facebook 提出了 Flux 架构的思想,引发了很多的实现。2015年,Redux 出现,将 Flux 与函数式编程 结合一起,很短时间内就成为了最热门的前端架构。
如果你不知道是否需要 Redux,那就是不需要它
只有遇到 React 实在解决不了的问题,你才需要 Redux
简单说,如果你的UI层非常简单,没有很多互动,Redux 就是不必要的,用了反而增加复杂性。
用户的使用方式非常简单 用户之间没有协作 不需要与服务器大量交互,也没有使用 WebSocket 视图层(View)只从单一来源获取数据 需要使用Redux的项目:
用户的使用方式复杂 不同身份的用户有不同的使用方式(比如普通用户和管理员) 多个用户之间可以协作 与服务器大量交互,或者使用了WebSocket View要从多个来源获取数据 从组件层面考虑,什么样子的需要Redux:
某个组件的状态,需要共享 某个状态需要在任何地方都可以拿到 一个组件需要改变全局状态 一个组件需要改变另一个组件的状态 Redux的设计思想:
Web 应用是一个状态机,视图与状态是一一对应的。 所有的状态,保存在一个对象里面(唯一数据源)。 注意:flux、redux都不是必须和react搭配使用的,因为flux和redux是完整的架构,在学习react的时候,只是将react的组件作为redux中的视图层去使用了。
18.3 redux使用三大原则 Single Source of Truth(唯一的数据源) State is read-only(状态是只读的) - 无法直接修改状态 Changes are made with pure function(数据的改变必须通过纯函数完成) src/13_redux/store.js 创建状态管理器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import { createStore } from 'redux' const reducer = (state = { msg: 'hello redux' , count: 10 }, action ) => { switch (action.type ) { case 'CAHNGE_MSG' : return { ...state, msg : action.payload } case 'INCREMENT_COUNT' : return { ...state, count : state.count + action.payload } case 'DECREMENT_COUNT' : return Object .assign ({}, state, { count : state.count - action.payload }) default : return state } } const store = createStore (reducer)export default store
src/index.js 配置状态管理器 - 状态管理器修改订阅视图的更新
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import store from './13_redux/store' import App from './13_redux/App' console .log (store)const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <App /> ) store.subscribe (() => { root.render ( <App /> ) })
src/13_redux/App.jsx使用状态管理器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import React from 'react' ;import Child1 from './Child1' ;import Child2 from './Child2' ;const App = ( return ( <div > <h1 > 使用redux</h1 > <Child1 /> <hr /> <Child2 /> </div > ); }; export default App ;
src/13_redux/Child1.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import React from 'react' ;import store from './store' const Child1 = ( const state = store.getState () return ( <div > <h3 > child1</h3 > <div > { state.msg } - { state.count } <button onClick ={() => { store.dispatch({ type: 'CAHNGE_MSG', payload: 'hello child1 redux' }) }}>修改msg</button > <button onClick ={ () => { store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT_COUNT', payload: 10 }) } }>加10</button > </div > </div > ); }; export default Child1 ;
src/13_redux/Child2.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import React from 'react' ;import store from './store' const Child2 = ( const state = store.getState () return ( <div > <h3 > child2</h3 > { state.msg } - { state.count } <button onClick ={() => { store.dispatch({ type: 'CAHNGE_MSG', payload: 'hello child2 redux' }) }}>修改msg</button > <button onClick ={ () => { store.dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT_COUNT', payload: 10 }) } }>减10</button > </div > ); }; export default Child2 ;
以上代码是最最最最最最最基本的redux的使用,现在企业里基本上不使用这种原始的方法
18.4 redux + react-redux配合使用 redux是属于js的状态管理模式,不独属于react,在react中需要结合 react-redux 模块使用
react-redux提供两个核心的api:
只要上层中有Provider组件并且提供了store, 那么,子孙级别的任何组件,要想使用store里的状态,都可以通过connect方法进行连接。如果只是想连接actionCreators,可以第一个参数传递为null
18.4.1 创建状态管理器 src/14_redux-react_redux/store.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import { createStore } from 'redux' const reducer = (state = { proList: [], kindList: [] }, { type, payload } ) => { switch (type) { case 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' : return { ...state, proList : payload } case 'CHANGE_KIND_LIST' : return { ...state, kindList : payload } default : return state } } const store = createStore (reducer)export default store
1.引入 createStore 方法(新版本中建议使用rtk)
2.创建reducer(包含初始化状态,包含了修改状态的标识,返回了新的状态(对象合并))
3.创建store
4.暴露store
18.4.2 使用react-redux src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import { Provider } from 'react-redux' import store from './14_redux_react-redux/store' import App from './14_redux_react-redux/App' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <Provider store = { store }> <App /> </Provider > )
使用了 react-redux 提供的组件组件 Provider 配合 store 完成传递数据
src/14_redux_react-redux/App.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import React from 'react' ;import Home from './Home' ;import Kind from './Kind' ;const App = ( return ( <div > <h1 > redux + react-redux</h1 > <Home /> <hr /> <Kind /> </div > ); }; export default App ;
src/14_redux_react-redux/Home.jsx 业务逻辑写到了组件中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 import React , { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { connect } from 'react-redux' ;const Home = (props ) => { console .log (props) const { proList, dispatch } = props useEffect (() => { fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/list' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => console .log (res.data ) dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) }, [dispatch]) return ( <div > <h3 > home</h3 > <ul > { proList && proList.map(item => { return (<li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname }</li > ) }) } </ul > </div > ); }; const mapStateToProps = (state ) => { return { proList : state.proList } } export default connect (mapStateToProps)(Home );
src/14_redux_react-redux/Kind.jsx 业务逻辑写到容器组件中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 import React , { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { connect } from 'react-redux' const Kind = (props ) => { const { kindList, getKindListData } = props useEffect (() => { getKindListData () }, [getKindListData]) return ( <div > <h3 > kind</h3 > { kindList && kindList.map(item => { return ( <p key = { item }> { item } </p > ) }) } </div > ); }; const mapStateToProps = (state ) => { return { kindList : state.kindList } } const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch ) => { return { getKindListData () { fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/categorylist' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => console .log (res.data ) dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_KIND_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) } } } export default connect (mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Kind );
vuex中 可以把异步操作提取到vuex中的actions中,react中异步操作方式会有很多,最常见的就是 redux-thunk
18.5 redux+react-redux分模块使用 如果项目很大,或者项目划分比较明确,需要将状态管理器也分模块去处理
假设现在有一个home模块,管理 bannerList 以及 proList
还有一个模块 kind 模块,管理 kindList
src/15_redux_react-redux_combine/store/modules/home.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 const reducer = (state = { bannerList: [], proList: [] }, { type, payload } ) => { switch (type) { case 'CHANGE_BANNER_LIST' : return { ...state, bannerList : payload } case 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' : return { ...state, proList : payload } default : return state } } export default reducer
src/15_redux_react-redux_combine/store/modules/kind.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const reducer = (state = { kindList: [] }, { type, payload } ) => { switch (type) { case 'CHANGE_KIND_LIST' : return { ...state, kindList : payload } default : return state } } export default reducer
整合多个reducer 为一个,因为 有一个原则 : 单一数据源 的原则
src/15_redux_react-redux_combine/store/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import { combineReducers, createStore } from 'redux' import home from './modules/home' import kind from './modules/kind' const reducer = combineReducers ({ home, kind }) const store = createStore (reducer)export default store
入口文件处引入状态管理器
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import { Provider } from 'react-redux' import store from './15_redux_react-redux_combine/store/index' import App from './15_redux_react-redux_combine/App' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <Provider store = { store }> <App /> </Provider > )
组件中使用状态管理器
src/15_redux_react-redux_combine/App.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import React from 'react' ;import Home from './views/Home' import Kind from './views/Kind' const App = ( return ( <div > <Home /> <hr > </hr > <Kind /> </div > ); }; export default App ;
src/15_redux_react-redux_combine/views/Home.jsx 业务逻辑在展示型组件中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 import React , { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { connect } from 'react-redux' const Home = ({ bannerList, proList, dispatch } ) => { useEffect (() => { fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/banner/list' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_BANNER_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/list' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) }, [dispatch]) return ( <div > <h1 > Home</h1 > <div > { bannerList && bannerList.map(item => ( <img key = { item.bannerid } src ={ item.img } alt ={item.alt} style ={{ height: 100 }} /> )) } </div > <ul > { proList && proList.map(item => { return (<li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname }</li > ) }) } </ul > </div > ); }; export default connect ( ({ home: { bannerList, proList } } ) => ({ bannerList, proList }) )(Home );
src/15_redux_react-redux_combine/views/Kind.jsx 业务逻辑在容器组件中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 import React from 'react' ;import { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { connect } from 'react-redux' const Kind = ({ kindList, getKindListData } ) => { useEffect (() => { getKindListData () }, [getKindListData]) return ( <div > <h1 > Kind</h1 > { kindList && kindList.map(item => { return ( <p key = { item }> { item } </p > ) }) } </div > ); }; export default connect ( ({ kind: { kindList }} ) => ({ kindList }), (dispatch ) => ({ getKindListData () { fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/categorylist' ).then (res =>json ()).then (res => dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_KIND_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) } }) )(Kind );
细心的你发现,虽然展示组件的代码变少了,但是容器组件中还有 异步相关操作,能否把这些异步操作提取出去
18.6 redux + react-redux + 分模块+ 异步操作 配合redux 常用的异步模块 为 redux-thunk, redux-saga
18.6.1 redux-thunk src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/store/modules/home.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 const reducer = ( state = { bannerList: [], proList: [] }, { type, payload } switch (type) { case 'CHANGE_BANNER_LIST' : return { ...state, bannerList : payload } case 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' : return { ...state, proList : payload } default : return state } } export default reducer
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/store/modules/kind.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 const reducer = ( state = { kindList: [] }, { type, payload } switch (type) { case 'CHANGE_KIND_LIST' : return { ...state, kindList : payload } default : return state } } export default reducer
整合多个reducer 为一个,因为 有一个原则 : 单一数据源 的原则
并且后续需要使用 异步操作,将异步操作模块 使用进来
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/store/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import { createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware } from 'redux' import thunk from 'redux-thunk' import home from './modules/home' import kind from './modules/kind' const reducer = combineReducers ({ home, kind }) const store = createStore (reducer, applyMiddleware (thunk))export default store
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import { Provider } from 'react-redux' import store from './16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/store' import App from './16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/App' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <Provider store = { store }> <App /> </Provider > )
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/App.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import React from 'react' ;import Home from './views/Home' import Kind from './views/Kind' const App = ( return ( <div > <Home /> <hr /> <Kind /> </div > ); }; export default App ;
上一个案例 异步操作在组件,现在需要将其放到 异步操作模块中去 actionCreator
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/api/home.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 export function getBannerList () { return fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/banner/list' ).then (res =>json ()) } export function getProList (params) { return fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/list?limitNum=' + params.limitNum ).then (res =>json ()) }
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/api/kind.js
1 2 3 export function getKindList () { return fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/categorylist' ).then (res =>json ()) }
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/store/actions/home.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import { getBannerList, getProList } from '../../api/home' const action = { getBannerListAction (dispatch) { getBannerList ().then (res => dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_BANNER_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) }, getProListAction (params) { return (dispatch ) => { getProList (params).then (res => dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) } } } export default action
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/store/actions/kind.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import { getKindList } from '../../api/kind' const action = { getKindListAction (dispatch) { getKindList ().then (res => dispatch ({ type : 'CHANGE_KIND_LIST' , payload : res.data }) }) } } export default action
记住接口有无参数影响 action 的写法,还影响其调用
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/views/Home.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 import React from 'react' ;import { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { connect } from 'react-redux' import action from '../store/actions/home' const Home = connect ((state ) => { return { bannerList : state.home .bannerList , proList : state.home .proList } }, (dispatch ) => { return { getBannerList () { dispatch (action.getBannerListAction ) }, getProList () { dispatch (action.getProListAction ({ count : 2 , limitNum : 3 })) } } })(({ bannerList, proList, getBannerList, getProList } ) => { useEffect (() => { getBannerList () getProList () }, [getBannerList, getProList]) return ( <div > <h1 > 首页</h1 > <ul > { bannerList && bannerList.map(item => ( <img src = { item.img } key = { item.bannerid } alt ="" style ={{ height: 60 }}> </img > )) } </ul > <ul > { proList && proList.map(item => ( <li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname }</li > )) } </ul > </div > ); }); export default Home ;
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/views/Home.jsx 异步在组件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 import React , { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { connect } from 'react-redux' import action from '../store/actions/home' const Home = ({ bannerList, proList, getBannerListData, getProListData } ) => { useEffect (() => { getBannerListData () getProListData () }, [getBannerListData, getProListData]) return ( <div > <h1 > Home</h1 > <div > { bannerList && bannerList.map(item => ( <img key = { item.bannerid } src ={ item.img } alt ={item.alt} style ={{ height: 100 }} /> )) } </div > <ul > { proList && proList.map(item => { return (<li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname }</li > ) }) } </ul > </div > ); }; export default connect ( ({ home: { bannerList, proList }} ) => ({ bannerList, proList }), (dispatch ) => ({ getBannerListData () { dispatch (action.getBannerListAction ) }, getProListData () { dispatch (action.getProListAction ({ limitNum : 2 })) } }) )(Home );
src/16_redux_react-redux_redux-thunk_combine/views/Kind.jsx 异步在store
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import React , { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { connect } from 'react-redux' import action from '../store/actions/kind' const Kind = ({ kindList, getKindListData } ) => { useEffect (() => { getKindListData () }, [getKindListData]) return ( <div > <h1 > Kind</h1 > { kindList && kindList.map(item => { return ( <p key = { item }> { item } </p > ) }) } </div > ); }; export default connect ( ({ kind: { kindList } } ) => ({ kindList }), (dispatch ) => ({ getKindListData () { dispatch (action.getKindListAction ) } }) )(Kind );
虽然引入了redux-thunk,但是仍然可以把 异步放在组件中,具体根据项目的需求而定
创建状态模块
整合模块
创建异步的 actionCreator
组件触发 actionCreator
传递数据以及修改界面
18.6.2 redux-saga 先要了解解决异步操作方案:回调函数、promise、async await、generator yield
https://es6.ruanyifeng.com/#docs/generator-async
src/17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/store/modules/home.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 const reducer = (state = { bannerList: [], proList: [] }, { type, payload } ) => { switch (type) { case 'CHANGE_BANNER_LIST' : return { ...state, bannerList : payload } case 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' : return { ...state, proList : payload } default : return state } } export default reducer
src/17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/store/modules/kind.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 const reducer = (state = { kindList: [] }, { type, payload } ) => { switch (type) { case 'CHANGE_KIND_LIST' : return { ...state, kindList : payload } default : return state } } export default reducer
src/17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/api/home.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 export function getBannerList () { return fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/banner/list' ).then (res =>json ()) } export function getProList (params) { return fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/list?limitNum=' + params.limitNum ).then (res =>json ()) }
src/17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/api/kind.js
1 2 3 export function getKindList () { return fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/categorylist' ).then (res =>json ()) }
src/17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/store/mySaga.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import { put, call, takeLatest } from 'redux-saga/effects' import { getBannerList, getProList } from '../api/home' import { getKindList } from '../api/kind' function * getBannerListAction () { const res = yield call (getBannerList) console .log ('banner' , res.data ) yield put ({ type : 'CHANGE_BANNER_LIST' , payload : res.data }) } function * getProListAction (action) { console .log (111 , action) const res = yield call (getProList, action.payload ) console .log ('pro' , res.data ) yield put ({ type : 'CHANGE_PRO_LIST' , payload : res.data }) } function * getKindListAction () { const res = yield call (getKindList) console .log ('kind' , res.data ) yield put ({ type : 'CHANGE_KIND_LIST' , payload : res.data }) } function * mySaga () { yield takeLatest ('REQUEST_BANNER' , getBannerListAction) yield takeLatest ('REQUEST_PRO' , getProListAction) yield takeLatest ('REQUEST_KIND' , getKindListAction) } export default mySaga
src/17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/store/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import { createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware } from 'redux' import createSagaMiddleWare from 'redux-saga' import mySaga from './mySaga' import home from './modules/home' import kind from './modules/kind' const reducer = combineReducers ({ home, kind }) const middleware = createSagaMiddleWare () const store = createStore (reducer, applyMiddleware (middleware)) middleware.run (mySaga) export default store
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import { Provider } from 'react-redux' import store from './17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/store/index' import App from './17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/App' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <Provider store = { store }> <App /> </Provider > )
src/17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/views/Home.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import React from 'react' ;import { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { connect } from 'react-redux' const Home = ({ bannerList, proList, dispatch } ) => { useEffect (() => { dispatch ({ type : 'REQUEST_BANNER' }) dispatch ({ type : 'REQUEST_PRO' , payload : { limitNum : 3 } }) }, [dispatch]) return ( <div > <h1 > Home</h1 > <div > { bannerList && bannerList.map(item => ( <img key = { item.bannerid } src ={ item.img } alt ={item.alt} style ={{ height: 100 }} /> )) } </div > <ul > { proList && proList.map(item => { return (<li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname }</li > ) }) } </ul > </div > ); }; export default connect ( ({ home: { bannerList, proList }} ) => ({ bannerList, proList }) )(Home );
src/17_redux_react-redux_redux-saga_combine/views/Kind.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import React , { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { connect } from 'react-redux' const Kind = ({ kindList, getKindListData } ) => { useEffect (() => { getKindListData () }, [getKindListData]) return ( <div > <h1 > Kind</h1 > { kindList && kindList.map(item => { return ( <p key = { item }> { item } </p > ) }) } </div > ); }; export default connect ( ({ kind: { kindList }} ) => ({kindList}), (dispatch ) => ({ getKindListData () { dispatch ({ type : 'REQUEST_KIND' }) } }) )(Kind );
18.7 使用immutable不可变数据数据结构 immutable不可变的数据解构,意思就是一旦数据被创建,需要使用特殊的方法进行修改(修改过后的数据也是符合immutable数据解构的,他是一个全新的对象)
学习immutable: https://www.npmjs.com/package/immutable
1 $ cnpm i immutable redux-immutable -S
重点就是修改 reducer 的数据机构以及组件中获取状态的方式(整合reducer时使用 redux-immutable 提供的 combineReducers)
拷贝17文件,修改 store/modules/home.js store/modules/kind.js store/index.js
views/Home.jsx views/Kind.jsx
https://cn.redux.js.org/
https://cn.redux.js.org/redux-toolkit/overview/
Redux Toolkit
它包括几个实用程序功能,这些功能可以简化最常见场景下的 Redux 开发,包括配置 store、定义 reducer,不可变的更新逻辑、甚至可以立即创建整个状态的 “切片 slice”,而无需手动编写任何 action creator 或者 action type。它还包括使用最广泛的 Redux 插件,例如 Redux Thunk 用于异步逻辑,而 Reselect 用于编写选择器 selector 函数,因此你可以立即使用它们。
https://cn.redux.js.org/tutorials/quick-start
1 $ cnpm i @reduxjs/toolkit redux react-redux redux-devtools -S
19.2.1 创建状态管理器 src/19_rtk/store/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' const store = configureStore ({ reducer : { } }) export default store
19.2.2 入口文件配置状态管理器 src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import { Provider } from 'react-redux' import store from './19_rtk/store' import App from './19_rtk/App' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <Provider store = { store }> <App /> </Provider > )
19.2.3 创建分模块切片 创建 slice 需要一个字符串名称来标识切片、一个初始 state 以及一个或多个定义了该如何更新 state 的 reducer 函数。slice 创建后 ,我们可以导出 slice 中生成的 Redux action creators 和 reducer 函数。
src/19_rtk/store/modules/home.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' export const homeSlice = createSlice ({ name : 'home' , initialState : { bannerList : [], proList : [] }, reducers : { changeBannerList (state, action) { state.bannerList = action.payload }, changeProList (state, action) { state.proList = action.payload } } }) console .log ('home' , homeSlice)export const { changeBannerList, changeProList } = homeSlice.actions export default homeSlice.reducer
src/19_rtk/store/modules/kind.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' export const kindSlice = createSlice ({ name : 'kind' , initialState : { kindList : [] }, reducers : { changeKindList (state, action) { state.kindList = action.payload } } }) export const { changeKindList } = kindSlice.actions export default kindSlice.reducer
19.2.4 整合切片 src/19_rtk/store/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' import home from './modules/home' import kind from './modules/kind' const store = configureStore ({ reducer : { home, kind } }) export default store
19.2.5 组件中使用状态管理器 src/19_rtk/views/Home.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 import React , { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux' import { changeBannerList, changeProList } from './../store/modules/home' import { getBannerList, getProList } from '../api/home' const Home = ( const bannerList = useSelector (state =>home .bannerList ) const proList = useSelector (state =>home .proList ) const dispatch = useDispatch () useEffect (() => { getBannerList ().then (res => dispatch (changeBannerList (res.data )) }) getProList ({ limitNum : 5 }).then (res => dispatch (changeProList (res.data )) }) }, [dispatch]) return ( <div > <h1 > Home</h1 > <div > { bannerList && bannerList.map(item => ( <img key = { item.bannerid } src ={ item.img } alt ={item.alt} style ={{ height: 100 }} /> )) } </div > <ul > { proList && proList.map(item => { return (<li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname }</li > ) }) } </ul > </div > ); }; export default Home ;
src/19_rtk/views/Kind.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import React from 'react' ;import { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux' import { getKindList } from '../api/kind' import { changeKindList } from '../store/modules/kind' const Kind = ( const kindList = useSelector (state =>kind .kindList ) const dispatch = useDispatch () useEffect (() => { getKindList ().then (res => dispatch (changeKindList (res.data )) }) }, [dispatch]) return ( <div > <h1 > Kind</h1 > { kindList && kindList.map(item => { return ( <p key = { item }> { item } </p > ) }) } </div > ); }; export default Kind ;
使用configureStore创建 Redux store
configureStore 接受 reducer 函数作为命名参数configureStore 使用的好用的默认设置自动设置 store为 React 应用程序组件提供 Redux store
使用 React-Redux <Provider> 组件包裹你的 <App /> 传递 Redux store 如 <Provider store={store}> 使用 createSlice 创建 Redux “slice” reducer
使用字符串名称、初始状态和命名的 reducers 函数调用“createSlice”
Reducer 函数可以使用 Immer 来“改变”状态
导出生成的 slice reducer 和 action creators
在 React 组件中使用 React-Redux useSelector/useDispatch 钩子
此时发现,组件中的异步操作在 组件内部调用,接下来需要研究如何将异步操作从组件提取出来
19.3 提取异步操作 19.3.1 自己定义请求函数 src/20_rtk_async/api/home.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 export function getBannerList () { return fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/banner/list' ).then (res =>json ()) } export function getProList (params) { return fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/list?limitNum=' + params.limitNum ).then (res =>json ()) }
src/20_rtk_async/api/kind.js
1 2 3 export function getKindList () { return fetch ('http://121.89.205.189:3001/api/pro/categorylist' ).then (res =>json ()) }
src/20_rtk_async/store/modules/home.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' import { getBannerList, getProList } from '../../api/home' export const homeSlice = createSlice ({ name : 'home' , initialState : { bannerList : [], proList : [] }, reducers : { changeBannerList (state, action) { state.bannerList = action.payload }, changeProList (state, action) { state.proList = action.payload } } }) export const { changeBannerList, changeProList } = homeSlice.actions export function getBannerListAction (dispatch) { getBannerList ().then (res => dispatch (changeBannerList (res.data )) }) } export function getProListAction (params) { return (dispatch ) => { getProList (params).then (res => dispatch (changeProList (res.data )) }) } } export default homeSlice.reducer
src/20_rtk_async/store/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' import home from './modules/home' const store = configureStore ({ reducer : { home } }) export default store
src/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import { Provider } from 'react-redux' import store from './20_rtk_async/store' import App from './20_rtk_async/App' const root = ReactDOM .createRoot (document .getElementById ('root' ))root.render ( <Provider store = { store }> <App /> </Provider > )
src/20_rtk_async/App.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import React from 'react' ;import Home from './views/Home' ;import Kind from './views/Kind' ;const App = ( return ( <div > <Home /> <hr /> <Kind /> </div > ); }; export default App ;
src/20_rtk_async/views/Home.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import React , { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux' import { getBannerListAction, getProListAction } from '../store/modules/home' const Home = ( const bannerList = useSelector (state =>home .bannerList ) const proList = useSelector (state =>home .proList ) const dispatch = useDispatch () useEffect (() => { dispatch (getBannerListAction) dispatch (getProListAction ({ limitNum : 8 })) }, [dispatch]) return ( <div > <h1 > Home20</h1 > <div > { bannerList && bannerList.map(item => ( <img key = { item.bannerid } src ={ item.img } alt ={item.alt} style ={{ height: 100 }} /> )) } </div > <ul > { proList && proList.map(item => { return (<li key = { item.proid }> { item.proname }</li > ) }) } </ul > </div > ); }; export default Home ;
19.3.2 使用 createAsyncThunk 请求数据 Redux Toolkit 的 createAsyncThunk API 生成 thunk,为您自动 dispatch 那些 “start/success/failure” action。
src/20_rtk_async/store/modules/kind.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import { createSlice, createAsyncThunk } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' import { getKindList } from './../../api//kind' export const kindSlice = createSlice ({ name : 'kind' , initialState : { kindList : [] }, reducers : { changeKindList (state, action) { state.kindList = action.payload } }, extraReducers : (builder ) => { builder .addCase (getKindListAction.pending , state => state.status = 'loading' }) .addCase (getKindListAction.fulfilled , (state, action ) => { state.status = 'idle' state.kindList = action.payload }) .addCase (getKindListAction.rejected , state => state.status = 'failed' }) } }) export const getKindListAction = createAsyncThunk ('kind/getKindListAction1123' , async (num) => { console .log ('num' , num) const res = await getKindList () return res.data }) export const { changeKindList } = kindSlice.actions export default kindSlice.reducer
src/20_rtk_async/views/Kind.jsx
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import React from 'react' ;import { useEffect } from 'react' ;import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux' import { getKindListAction } from '../store/modules/kind' const Kind = ( const kindList = useSelector (state =>kind .kindList ) const dispatch = useDispatch () useEffect (() => { dispatch (getKindListAction (1000000 )) }, [dispatch]) return ( <div > <h1 > Kind20</h1 > { kindList && kindList.map(item => { return ( <p key = { item }> { item } </p > ) }) } </div > ); }; export default Kind ;